Table of Contents (click to expand)
The light from lighthouses can be seen from miles away because of the design of the light system. The system was designed by Augustin Fresnel and it uses lenses and reflectors to capture and concentrate light to a specific point, making it quite powerful. The lenses used in the system are very thin and they capture more light from a light source, which increases the intensity of the lamp. The light beam emitted by the system is visible over 20 miles (32 kilometers) away.
Lighthouses have been an object of adoration and fascination for many poets and storytellers for hundreds of years. This should come as no surprise, as these tall, forlorn structures of the sea have been guiding ships and sailors for generations, not only in peaceful waters, but also in the most difficult and challenging situations.
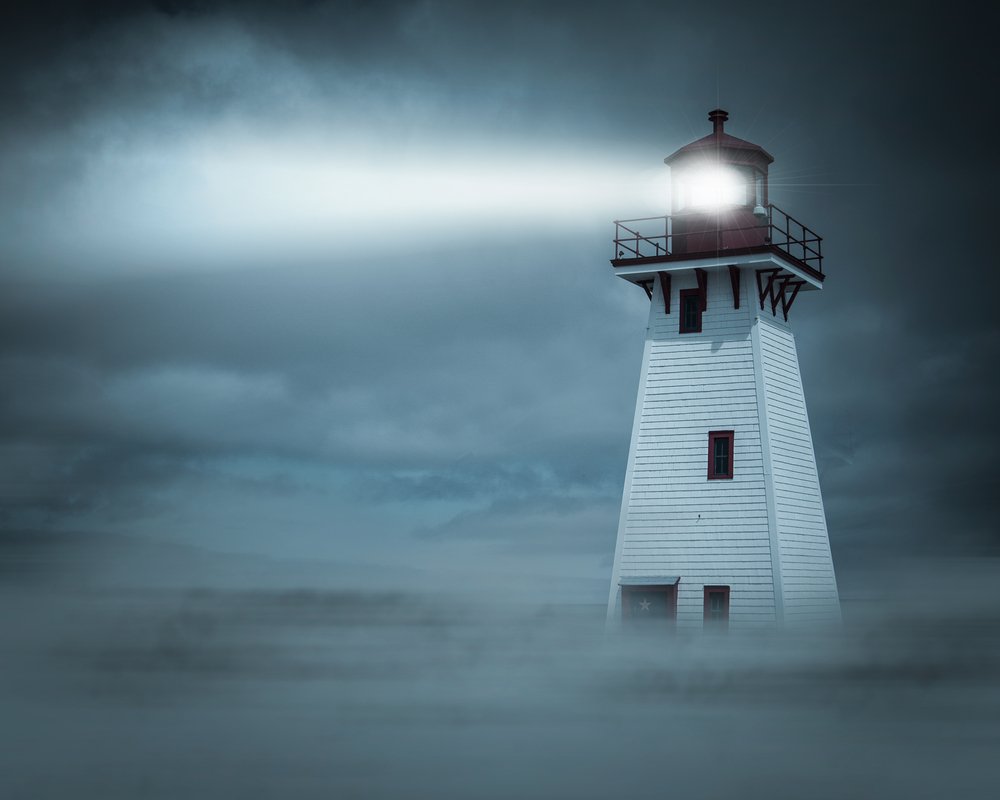

A strong beam emitted by a lighthouse is an astounding navigational aid to many ships and boats at sea. Have you ever wondered what allows the light emitted by a lighthouse to be seen by sailors who are many miles away? Is that a magic light or is there some kind of science acting behind it?
Recommended Video for you:
What Is A Lighthouse?
A lighthouse is a tall building (usually a tower-like structure) that contains a set of lamps and lenses that emit strong beams of light to aid navigation at sea. This light is visible over long distances and helps to guide ships toward safe harbor or away from dangerous rocks.
To support the main function of a lighthouse, which is producing a light beam, a lighthouse used to contain heavy and cumbersome systems that ensured that the light glowed both day and night. In addition to this, a lighthouse will often have a boathouse, a fog signal building, living quarters for the keeper of the system, and an oil house.
Construction Of A Lighthouse
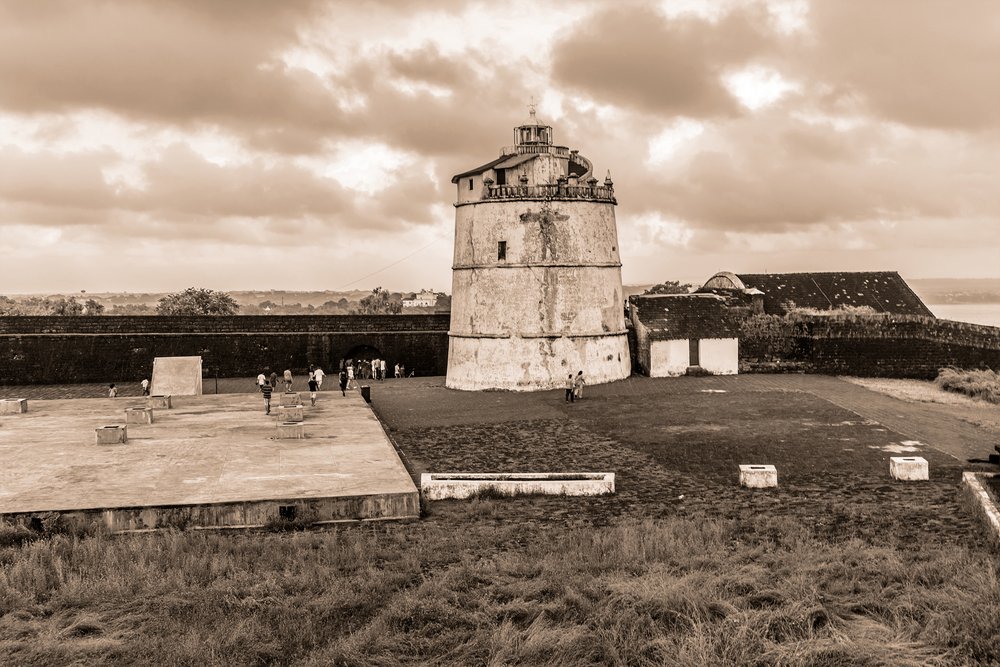

It is said that no two lighthouses are the same. In the past, lighthouses were built using the materials that were available locally and easily, such as wood, cast iron, brick, stone, concrete and various other substances. The site construction of a lighthouse can also vary significantly. Some are constructed onshore overlooking the water, while others are built offshore on small patches of rocks. The heights can also vary suite a bit. For example, if you are building a lighthouse on a cliff that is quite tall, you don’t need to make it too tall, as the height of the cliff already boosts the height of the lighthouse.
Design Of The Light System
This brings us to our first questions, what makes the light glow so brightly?
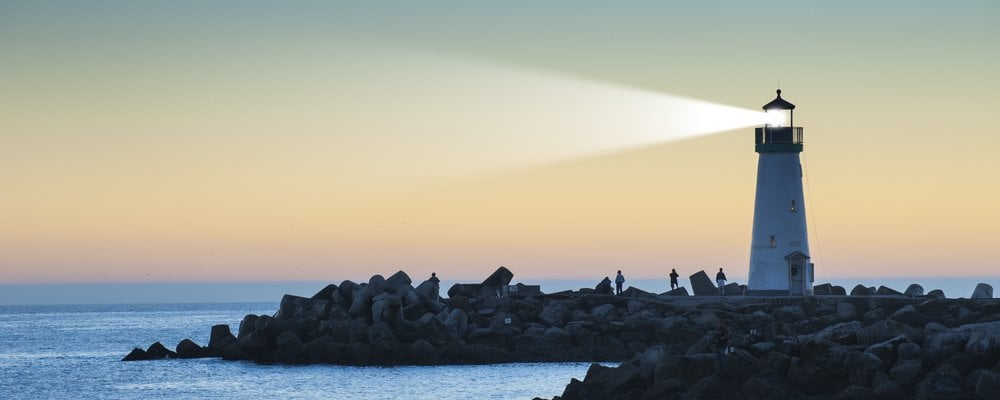

The function of a lighthouse all comes down to the intensity of the light. A French inventor, Augustin Fresnel, had deduced that light was actually a kind of energy that travels in the form of waves (which was not commonly known at the time). Given that light travelled in waves, it was possible to make them converge on a single point or deflect from a certain point in different directions. He used this principle to make lenses and reflectors that were capable of capturing and then concentrating light to a specific point, making it quite powerful.
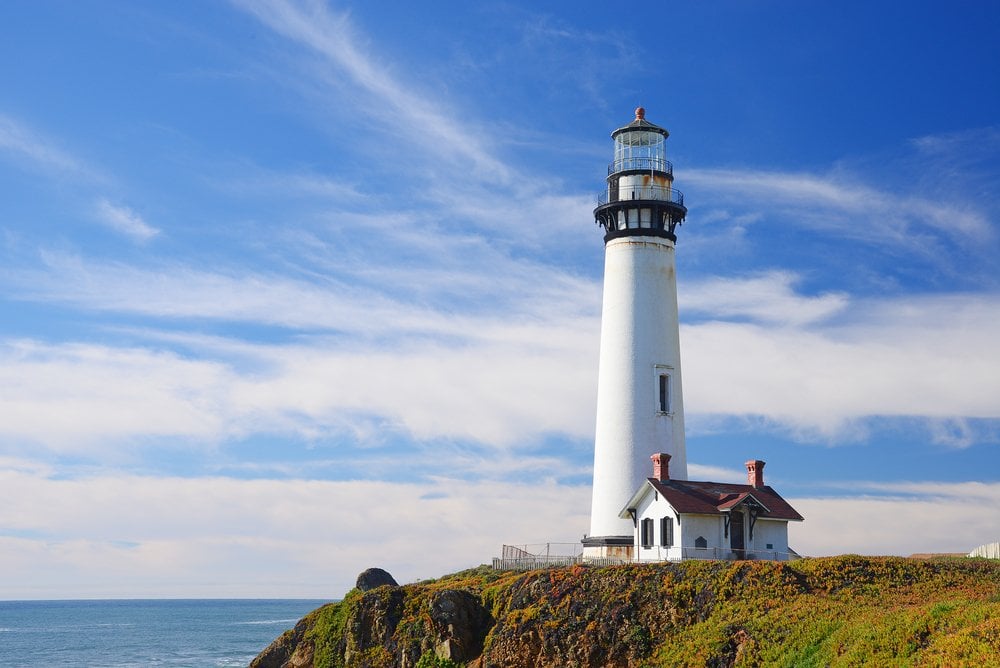

Fresnel also made lenses that had high aperture and low focal length. The lenses he made were also very smaller in comparison to conventional lenses present at that time (in some cases, as thin as a sheet of glass). Finally, and what makes them so special, is that a Fresnel lens could capture more light from a light source and thus increase the intensity of the lamp.
The first lighthouse system that Fresnel made consisted of highly polished prisms and an array of such lenses in a concentric arrangement. The light rays contained within this system from the source were combined together (using the lenses) and thus the combined intensity was much greater than the light source itself.
The light beam emitted by such an ingenious system is visible over 20 miles (32 kilometers) away!
Following the advent of more automatic technologies, the presence of lighthouse keepers and other resources became less desirable, as automatic lamp changers emerged, eliminating the need for such traditional measures. Fortunately, the great design presented by Fresnel is still applied in lighthouses around the world and guides innumerable people at sea to this day.