Both optical and electron microscopes are governed by similar principles. If we take the quality of the ultimate image as the parameter of judgment, then electron microscopes produce far better images than optical ones.
Our eyes give us the vision we need to connect with the world around us. In the field of science, the discovery of the microscope has given many scientists the ability to look deep into the microscopic world and make some remarkable discoveries, such as that of the cell by Robert Hooke.
Recommended Video for you:
What Is A Microscope?
The term ‘microscope’ is derived from the Greek words for ‘small’ and ‘to view’. Thus, it is a device with which we can view small objects.
A microscope comes in two main types, depending on the construction: simple microscopes and compound microscopes.
A simple microscope uses only a single lens to obtain a magnified image. When using this microscope, the ultimate quality of the image is not very good, which is why it is not used for scientific studies.

On the other hand, a compound microscope is an arrangement that uses more than one lens to produce a magnified image of an object. It produces a high-resolution image of the object and is therefore ideal for scientific research purposes, laboratory and forensic purposes, and general industrial uses.
The two types of lenses used in the compound microscope are the objective lens and the eyepiece. The objective lens is placed facing the object to be examined, while the eyepiece is the lens through which the image is viewed. The eyepiece is also referred to as an ocular lens.
When the light passes through the objective lens from the object, a magnified, real image is produced. This image is further magnified by the eyepiece lens and a virtual image is produced when seen through the eyepiece, making greater detail visible.
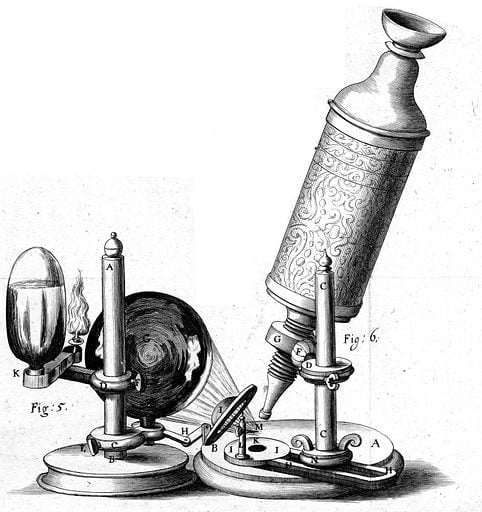
Microscopes are classified based on the kind of method they use to scan or examine the object.
What Is An Optical Microscope?
As the name suggests, an optical microscope uses light as the medium to scan objects, and through the system of lenses produces a magnified image. It is also called a ‘light microscope’. This is the most common type of microscope and finds use in various fields. They are relatively easy to construct and work with.
Since it generally uses visible light, the image produced can be directly perceived by the human eye.
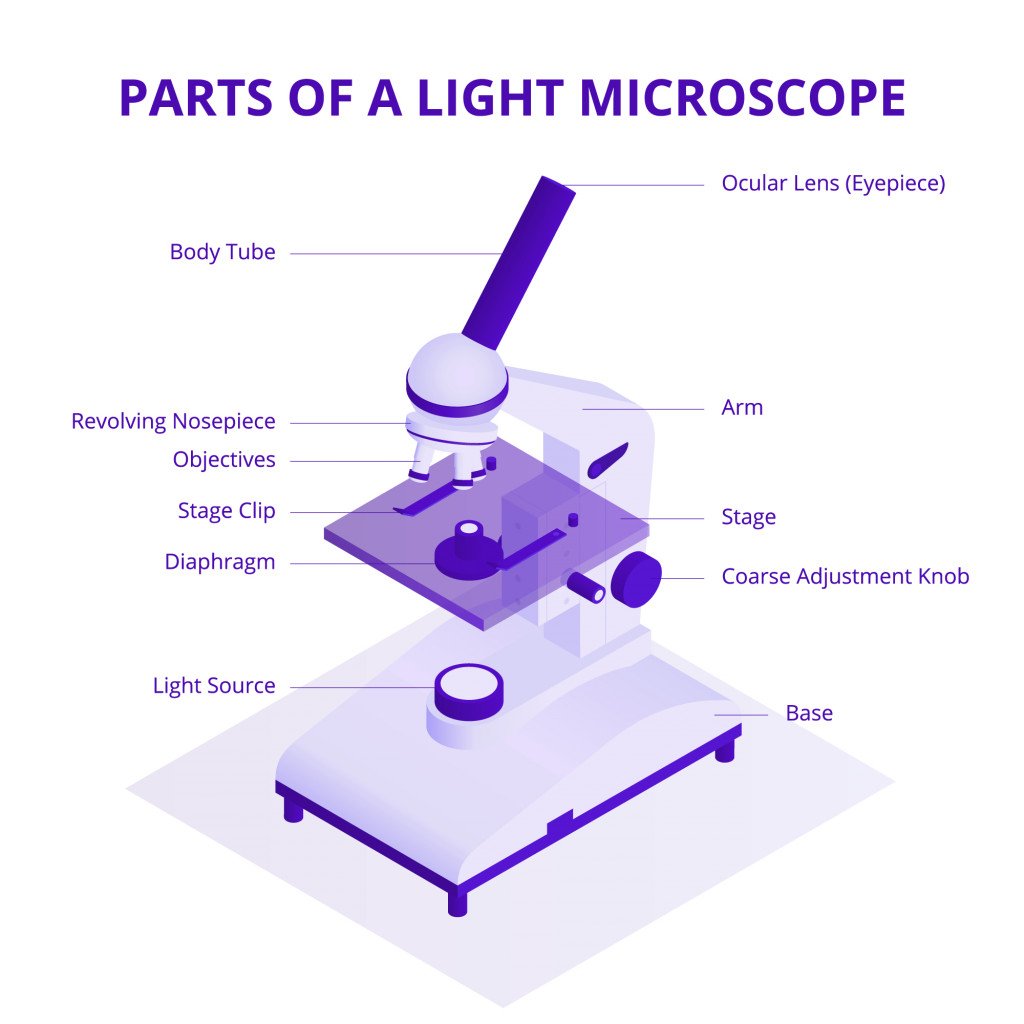
In a compound optical microscope, the amount of light on the sample can be increased or decreased, which in turn increases or decreases the resolution of the obtained image.
What Is An Electron Microscope?
An electron microscope uses an accelerated beam of electrons as the source of illumination of the specimen, and produces a very high-resolution image. Since the wavelength of electrons is extremely small, the resolving power of the microscope is very high.
Although the construction of this microscope is complicated, the image that it produces is incredibly detailed and not affected by atmospheric factors. Thus, this kind of microscope is used to study the internal structure and chemical composition of materials.
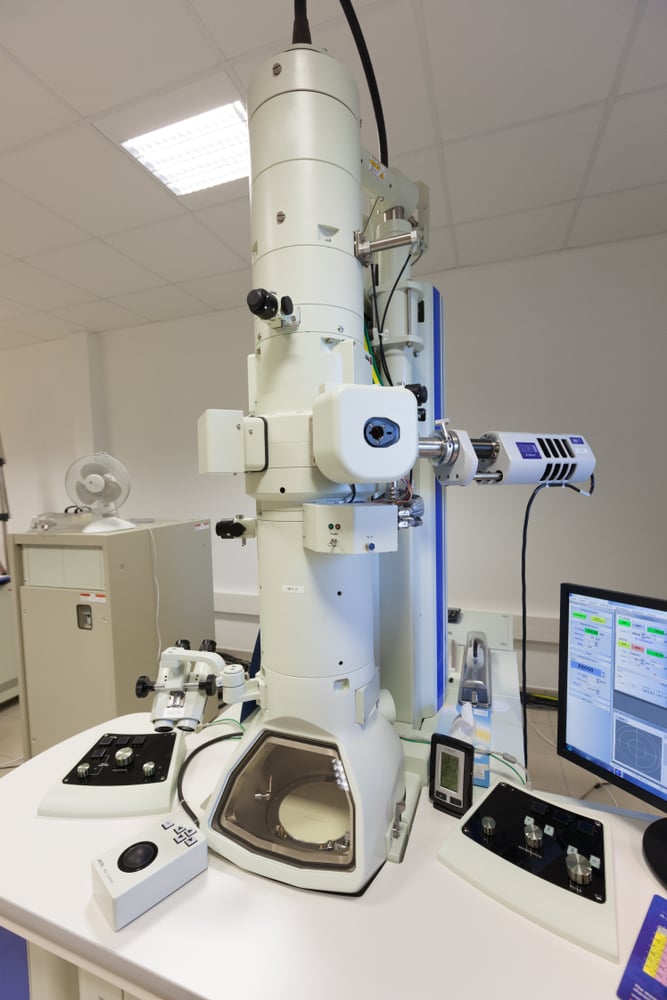

Electron microscopes are further divided into two types: the Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) and the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). Both of these are widely used in scientific and medical research.
Which Is Better: Optical Microscope Or Electron Microscope?
Both kinds of microscopes have their fair share of advantages and disadvantages. It is completely dependent on the usage and tasks to which they are assigned.
While the electron microscope has higher resolving power and produces higher resolution images than the optical microscope, it requires a vacuum to work. Also, the specimen preparation and the image production take a longer time than in an optical microscope. There is also a risk of radiation leakage involved with using an electron microscope.
On the other hand, the optical microscope is lighter and easier to use, but the image produced might not be suitable for the detailed study of internal structures. There are also higher chances of distortion in the image, due to the interference of atmospheric factors.
One must choose wisely between the two, keeping in mind the tasks you need to complete.
Future Developments In Microscopy
It is anticipated that microscopes will soon be supported with sophisticated algorithms that will help in even better interpretation of the images and the drawing of integrated conclusions. Scientists and researchers will be able to fully inspect and visualize three-dimensional models of the obtained image and gain better insight.
Resolution, speed, accuracy, and sensitivity are the key areas of focus in microscopy, at present and in the near future.
Conclusion
Each little step, each thought towards a broader vision, improves the possibilities of evolution. When we have the curiosity to look beyond what our physical senses have to offer, revolutionary discoveries inevitably occur!

The microscope is one such discovery that gave the correct tool to scientists and researchers, who then opened the closed doors to the microscopic world. With further advancements in Science and Engineering, the unknown areas of the microscopic world will be even more accessible to us.
References (click to expand)
- What Is an Electron Microscope (EM) and How Does It Work?. The United States Department of Veterans Affairs
- Microscopes - National Geographic Society. National Geographic
- The Evolution of the Microscope - JSTOR Daily. JSTOR
- MW Davidson. OPTICAL MICROSCOPY - Zeiss Campus. Florida State University
- Types of electron microscope - Science Learning Hub. sciencelearn.org.nz
- Future of Microscopes. futureforall.org