The moon is bright enough to appear during the daytime and the duration for which it is above the horizon of Earth coincides with the sun, making it possible to be seen during the daytime.
In my childhood, I knew the moon as the celestial entity that emerged only at night, after the sun departed, following its daytime duty! It was only in my early teens—as I learned more about science—that this dogma was dispelled. Before that, I was fully convinced that the moon was inseparably linked to the night sky. I never turned on my observatory mode to actually witness that the moon could also sometimes be visible during the day!
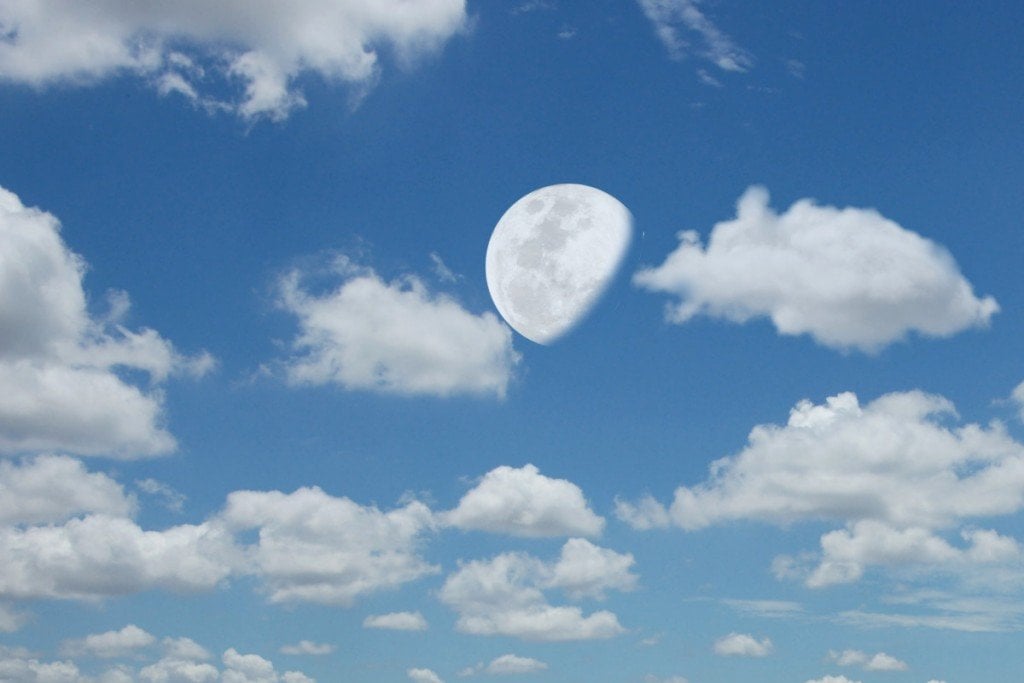

If you are still living under the assumption that the moon can only be seen in the night sky, you’re incorrect! The fact is that the moon is always hanging around our planet; sometimes it’s visible during the day (given you have the right climatic conditions) and other times it is visible during the night.
Primarily, there are two reasons why we sometimes see the moon during the day. First of all, the moon is bright and close enough to be seen against the blue hue of the sky. Secondly, the duration for which it is above the horizon of Earth coincides with the sun, making it possible to be seen during the daytime. Let’s look into these two reasons in more detail to understand the science of moon sightings during the day.
Recommended Video for you:
The Moon Is Bright Enough To Appear During The Daytime
Many of you might feel that the moon, like the stars, cannot be seen during the day. It’s true that we cannot see stars during the day, except in the very early morning, before the sun fully rises. The common explanation for this is that the faint glow of stars is washed out by the incredible illumination of the sun in the sky. Nerds would go a step further and explain that the stars are actually washed out because of the Earth’s atmosphere, which scatters the sunlight reaching our planet. However, the moon is no star, and since it’s not a star, it does not give off its own light. It simply reflects the light coming from the sun in order to illuminate itself.
It is worth noting that the moon is actually quite dark and only between 3%-12%of the sunlight hitting the lunar surface is reflected. However, owing to its close proximity to the Earth and its significant size, even this scanty portion of reflected light is bright enough to make the moon visible during the day. However, there are conditions applied to when it is visible during the day, as explained below.
The Role Of Earth’s Rotation In The Appearance Of The Moon During The Daytime
Earth and the moon are both always on the move. Besides revolving around the sun, Earth also rotates around its axis, and the moon simultaneously orbits around the Earth. The moon takes roughly 30 days to make a full orbit of the Earth.
Thus, the visibility of the moon from Earth depends entirely on the former’s position in its orbit. As the moon completes a revolution or an orbit around Earth in approximately 30 days, it appears in different shapes, depending upon where it is located with respect to the sun and Earth. These varied shapes are commonly referred to as the eight phases of the moon.
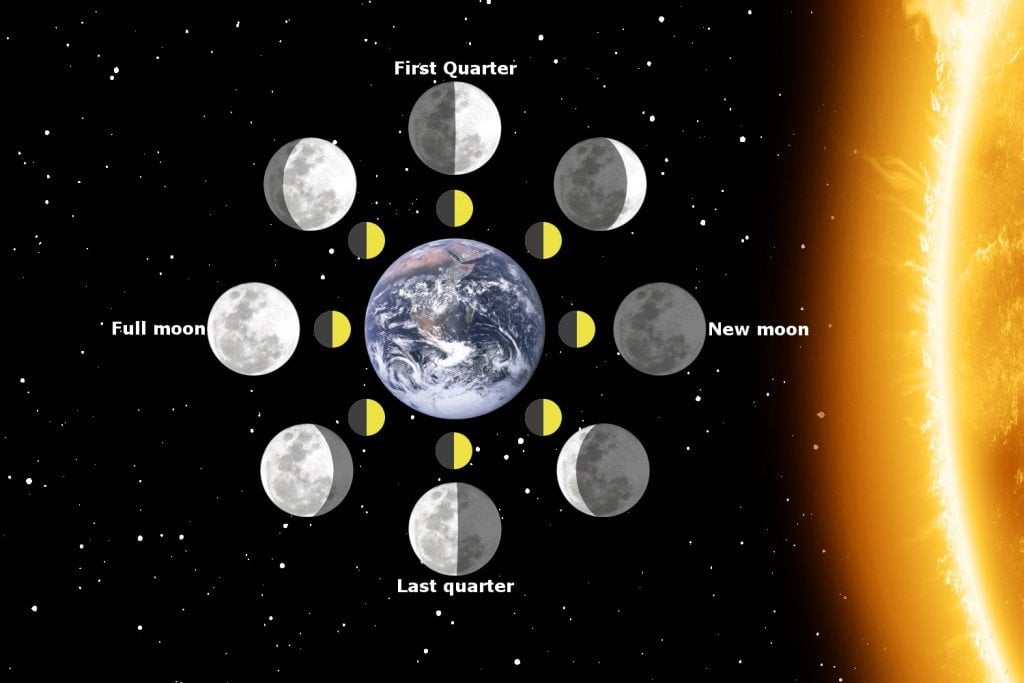
As mentioned earlier, the most important reason why we can even see the moon in the sky is because of the sun. As the sun is a star, it is capable of producing its own light. Basically, the moon is seen because upon reception of light from the sun, some portion of this light bounces off from the moon’s surface back to the Earth. Now, depending on the position of the moon in its orbit around the Earth, the lit-up portion of the moon becomes visible. As the moon comes in line with Earth and the sun—with Earth in between the moon and the sun—we can see a full moon.
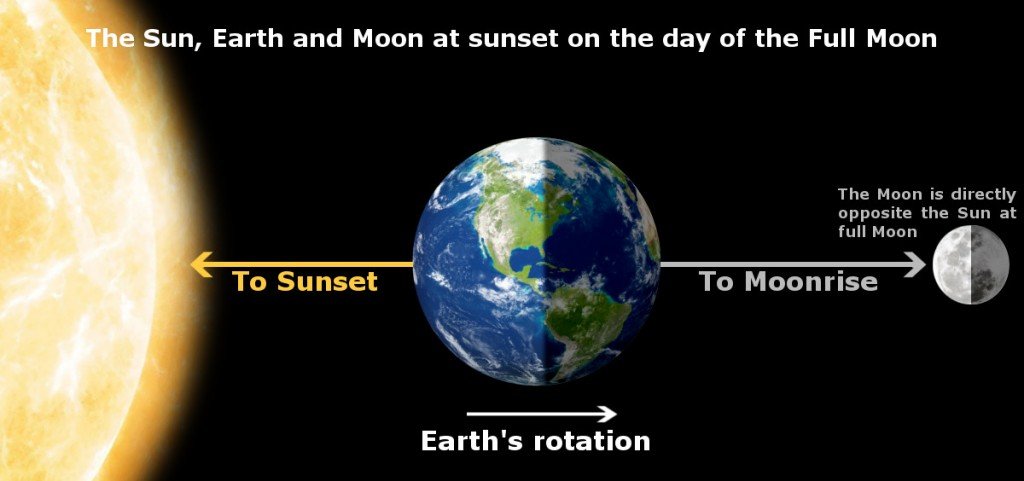
During a given portion of that time period (around the time of the full moon), the moon rises as the sun sets because the moon is directly opposite from the sun in the sky. Therefore, during every full moon, the sun, moon, and Earth line up in such a manner that we can watch the sun setting and the moon rising (on the opposite side of the horizon) at roughly the same time.
However, with each passing day, as its orbital cycle progresses, the moon keeps getting nearer to the sun until finally, it appears to be very close (around the time of a new moon), rising and setting almost at the same time as the sun. The upshot of this is that the moon becomes less visible at night, and more visible during the daytime!
Since the Earth is constantly rotating, the moon appears above the horizon for around 12 hours out of the total 24. On some days, these 12 hours coincide with the sun’s 12 hours above the horizon, at which points we can see the moon during the daytime!

After that point, the moon begins to move away from the sun until it gets back to the full moon phase and the cycle starts all over again.
Climatic Conditions
Although it’s interesting to note that the moon can be spotted during the daytime, its visibility is dependent on the climatic conditions too. The horizon also needs to be taken into consideration. In the case of typical British weather, lots of cloud cover, glimpsing the moon during the day would be quite difficult. However, for someone in the prairies of North America with big clear skies dominating one’s sight lines, there’s a much better chance of spotting the moon in broad daylight.
A Final Word
For all you stargazers out there, the moon appears in the daytime sky after the full moon phase until a few days before the new moon (it’s not visible around the new moon phase, as the illuminated side of the moon is facing away from the Earth). If you keep track of the phases of the moon on a daily basis (here’s a useful link), you will know the exact days when you can spot that faintly luminous, whitish ball during the daytime, provided the conditions are right!













