Table of Contents (click to expand)
The material a balloon is made out of has a lot to do with why it pops when pricked with a needle. A balloon made out of rubber or latex will pop because the material is elastic. The air inside the balloon is under more pressure than the air outside, so when a hole is made, the rubber around the hole is not being pulled uniformly in all directions. This causes the net force to pull the skin away from the hole, which further increases the size of the hole. The process is quick and the balloon will pop with a loud noise.
Popping balloons before, during and after birthday parties is one of my fondest memories of childhood. There’s something inexplicably satisfying about pricking a balloon and watching it go ‘Pop!’ in the very next instant.
But what goes on “behind the scenes” when you prick a balloon? Why does it pop instantaneously, rather than leaking air slowly, which is what happens when you prick a bag of chips?
Short answer: an inflated balloon’s “skin” is under a lot more tension, so it pops as soon as it’s poked, since the rubber around the pricked hole is not being pulled uniformly in all directions.
Recommended Video for you:
The Elasticity Of A Balloon
A balloon is usually made from highly elastic materials, such as rubber, latex, nylon or polychloroprene, which lends them the ability to inflate and stretch to become many times larger than their original size. The air inside the balloon is at a higher pressure than the air outside, which is why there’s a pressure differential between the inside and outside air.
The rubber in the balloon contains a number of long molecules (called ‘polymers’) that are linked together, just like how noodles in a plate tend to stick together. Due to their elastic nature, a balloon can be inflated up to a certain limit. If that limit is crossed, however, the tension pulling on the cross-links of the chains becomes too great, causing them to break – and Pop! goes the balloon.
How Does Popping A Balloon Work?

The moment you prick a balloon, a tiny hole is made on its surface. Now, if it’s only slightly inflated, it wouldn’t pop instantly; the air would leak out of it slowly until it was completely deflated, returning to its original size.
However, if it’s a balloon that has been inflated to its maximum size, its polymer chains are under a lot of tension. Every point on the surface is being uniformly pulled in all directions by the surrounding rubber molecules, keeping the balloon tightly stretched out. The moment a tiny hole appears on the surface, the rubber immediately surrounding the hole is suddenly no longer being pulled uniformly in all directions.
This causes the net force to pull the skin away from the hole, which further increases the hole’s size. This goes on until the entire skin of the balloon is pulled all the way back to a point opposite the hole and the balloon explodes with a popping sound. Note that the “pop” is attributed to the pressure wave created after a sudden pressure change due to the rapid expansion of the air that was inside the balloon.
When explained like this, it might seem like a long process, but it’s actually an incredibly quick one. Ask yourself this – how long does it take a balloon to pop from the time you poke it with something sharp? Exactly…. so this seemingly long process is essentially instantaneous.
Why Does A Balloon Pop When It’s Squirted With An Orange Peel?
If you’ve never tried this before, you might want to try it now. Take an orange peel and squirt some of the zest on an inflated balloon. If you’re not using a balloon that has vulcanized rubber in it, the balloon will pop instantly. Here’s a quick video of the experiment:
Why does that happen?
This strange phenomenon is because oranges consist of a colorless liquid hydrocarbon called limonene (which, by the way, also gives oranges their characteristic fragnance).
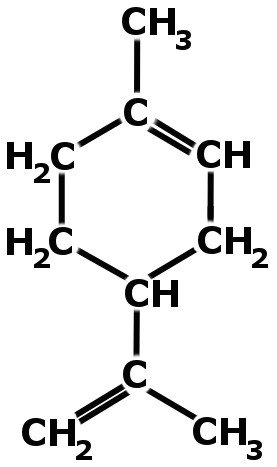
The non-polar nature of limonene is responsible for dissolving the non-polar chains present in rubber (where polymer strands are not cross-linked). If, however, the balloon is made of vulcanized rubber, it wouldn’t burst as a result of orange peels, because vulcanized rubber has its polymer strands connected by sulfur atoms.
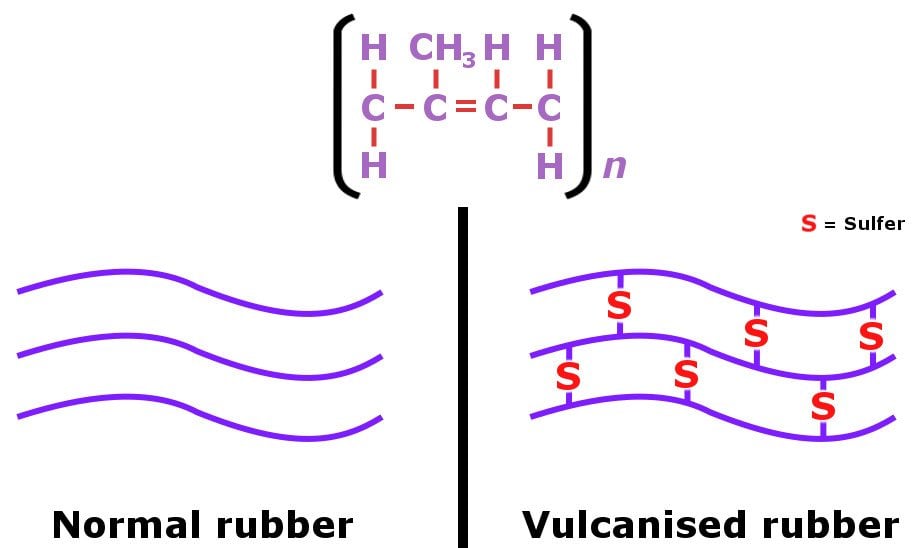
So, the next time you’re at a kid’s birthday party and want to pop balloons with a bit more style, make it a point to carry a few fresh oranges in your pockets. And yes, keep your fingers crossed that the balloons aren’t made of vulcanized rubber!
References (click to expand)
- Balloon - Wikipedia. Wikipedia
- Limonene - Wikipedia. Wikipedia
- When you put a balloon filled with water over a flame such as a candle, why doesn't the balloon pop or burst? - UCSB Science Line. The University of California, Santa Barbara
- Needle Through a Balloon - scifun.chem.wisc.edu:80
- How Does an Orange Peel Pop a Balloon? Chemistry, of .... chemedx.org













