Table of Contents (click to expand)
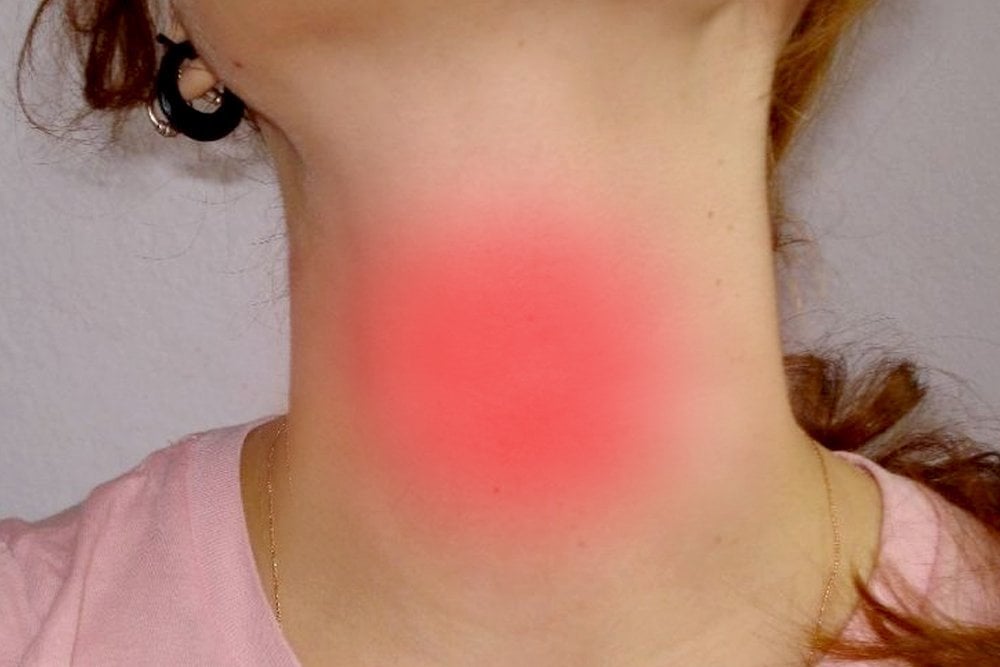
Odynophagia is a disorder that makes swallowing food/beverages painful. Common symptoms include burning pain and stabbing sensation in the mouth, throat, or esophagus. There are numerous medical conditions that can lead to odynophileia.
Odynophagia is a disorder that makes swallowing food/beverages painful. Do you incessantly feel pain in your throat, mouth, or food pipe (esophagus) when swallowing food, liquid, or even your own saliva? If so, you might be suffering from odynophagia. While odynophagia resolves quickly in many cases, if it persists for an extended period of time, that can be an indication of a more serious health condition.
There is not a single cause nor a singular effective treatment for odynophagia. This is because painful swallowing can be caused by various underlying health conditions. Below we will explain some of the most common medical conditions that can cause painful swallowing and what the remedies are for such conditions.
Recommended Video for you:
Odynophagia Vs Dysphagia
Odynophagia is often confused with dysphagia. Dysphagia is a different condition that primarily involves difficulty in swallowing, but it is often painless. Odynophagia is when the swallowing becomes painful. At times, this can be so painful that it is almost impossible to eat due to uncontrolled discomfort and pain.
Which is more critical of the two, you may wonder? Oddly enough, dysphagia is often more critical than odynophagia, as dysphagia can cause coughing or choking. In extreme situations, this can result in irritation or the breeding of bacteria in the lungs. This breeding can further aggravate the situation by causing disorders like pneumonia.
Although this is uncommon, dysphagia and odynophagia may occur at the same time. They may also have the same underlying causes. A good rule of the thumb is that if you only have swallowing difficulties, without any accompanying painful sensation, then it is most likely dysphagia. However, if you experience both difficulty or blockage when consuming food/liquid, alongside sharp pain, then you might have a combination of odynophagia and dysphagia. It is important to understand that odynophagia and dysphagia can be caused by inflammation or infection.
There is one more condition, called phagophobia, which might also be confused with odynophagia. Phagophobia is technically not a disorder, but rather a fear of swallowing and the expectation that you might not be able to swallow. There are often no physical symptoms to this condition; it’s typically a problem generated solely by the mind of the sufferer.

Symptoms
Odynophagia symptoms can be short-term or long-term, depending on the cause of pain. Common symptoms of odynophagia are as follows:
- Sharp burning pain, stabbing sensation in the mouth, throat, or esophagus when swallowing food items.
- Pain that typically worsens upon swallowing small, hard food items, such as dry fruit. In some cases, however, liquids and soft food might also make swallowing painful.
- If the pain is aggravated over time, it might be difficult to swallow some food items, which might manifest in the form of weight loss.
- Dehydration from reduced fluid intake is another symptom of odynophagia, as drinking some drinks/beverages might be painful.
It must also be noted that when an infection causes odynophagia, a person may notice other symptoms, such as fever and fatigue, or a general feeling of being unwell.
Causes
More often than not, odynophagia is a minor condition tantamount to a common cold. In such cases, painful swallowing will cure itself naturally in its own time. However, chronic painful swallowing may be a harbinger of other underlying complications. There are numerous medical conditions that can lead to odynophagia. Some of the most common causes of odynophagia are summarized as:
- Infections: Infections like the common cold or strep throat are some of the common causes of odynophagia. Some people may even develop candida infections in the mouth, throat or esophagus. Candida infections are actually fungal infections that usually target people with weak immune systems.
- GERD: This develops from the lower sphincter in the esophagus not being able to close properly. Due to the blockage, stomach acid leaks back into the esophagus. You might have GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) if you experience painful swallowing along with other signs, such as chest pain or heartburn.
- Esophageal cancer: Esophageal cancer is usually associated with persistent odynophagia and dysphagia, as well as inadvertent weight loss. Someone with esophageal cancer often complains about pain in their chest when swallowing.
- HIV: Odynophagia is much more common in people suffering with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). This is because antiretroviral agents used to treat HIV often result in acid reflux. This can, in turn, pave way for other complications like odynophagia. Also, as HIV patients already suffer from a weakened immune system, their bodies are much more vulnerable to odynophagia.
Types
Based upon recent studies and surveys by medicinal practitioners, odynophagia is classified into three categories:
- Ulcerative: This is characterized by ulcer formation with shallow or smooth edges in the esophagus. This is the most common variety observed in patients suffering from odynophagia
- Hyperplastic: This involves a florid fibrotic reaction (for simplicity, think of something like rashes) resulting in luminal narrowing in the esophagus and stricture formation.
- Granular: This category consists of multiple, small, miliary, mucosal granulomas. Granulomas are formations of granulation tissue in response to inflammation caused by foreign objects inside the body.
Treatment
The treatment for odynophagia is dependent on the underlying cause. Oral medications are usually the first route of remedy. For example, medicines used to treatment of GERD can also help in preventing stomach acid from creeping back up into the pharynx and esophagus. In turn, patients notice improvements in pain upon swallowing food items. People suffering with candida infections are usually given anti-fungal treatments. However, in extreme cases where there is the development of esophageal tumors or carcinoma, a doctor may recommend the surgical removal of these harmful cells.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that odynophagia, more than a condition, is a symptom in itself. Therefore, before you start looking for treatments to overcome this difficulty in swallowing, you should visit a doctor and obtain an accurate diagnosis. Information provided here is only for educational purposes; you will still need to consult a certified medicinal practitioner before following any of the advice in this article.
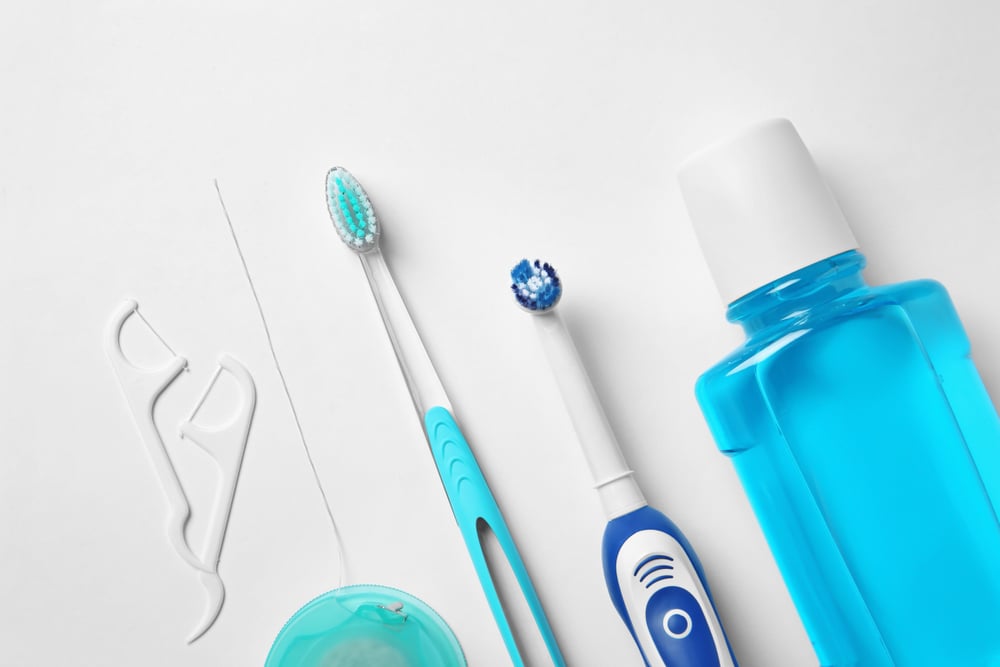

While medical treatment becomes essential if odynophagia becomes chronic and painful, prevention is always the best option. That prevention starts with your diet. An unhealthy diet can often be the primary cause, but eliminating certain unhealthy foods from your plate can sometimes be good enough. Additionally, it’s important to maintain good dental hygiene. This is because the bacteria from your mouth can reach other surrounding structures and organs, leading to unwanted infections. In the case of a non-vegetarian diet, you should pay attention to the foods you are eating, especially certain types of fish.
References (click to expand)
- Slee, G. R., Wagner, S. M., & McCullough, F. S. (1985, June 15). Odynophagia in patients with malignant disorders. Cancer. Wiley.
- Ban, K. M., Sanchez, L. D., Bramwell, K., Sakles, J. C., Davis, D., Wolfe, R., & Rosen, P. (2007, September 28). A 36-year-old man with odynophagia. Internal and Emergency Medicine. Springer Science and Business Media LLC.
- Infections of the Esophagus, Stomach, and Duodenum.