Table of Contents (click to expand)
Facial recognition technology is used to discern and identify human faces from an image or video. A system employed to perform facial recognition uses biometrics to map facial features from the photo or video. It compares this information with a large database of recorded faces to find a correct match.
Facial recognition is an advanced technology that helps in discerning and identifying human faces from an image or video. A system employed to perform facial recognition uses biometrics to map facial features from the photo or video. It compares this information with a large database of recorded faces to find a correct match.

Facial recognition is touted to be one of the top 3 methods of biometric recognition to identify people by measuring some aspect of individual physiology or anatomy. Facial recognition is the fastest-growing biometric technology and is expected to grow to $7.7 billion by 2022. This is because facial recognition has a wide range of commercial applications and is relatively simple to set up. It can be used for everything from surveillance to targeted marketing.
Recommended Video for you:
History Of Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology gained popularity in the early 1990s when the United States Department of Defense was seeking a technology that could spot criminals who furtively crossed borders. The Defense Department roped in eminent university scientists and experts in the field of facial recognition for this purpose by providing them with research financing.
Facial recognition made bold headlines in early 2001 immediately after it was first used in a public space—at Super Bowl XXXV in Tampa—by the law enforcement authorities to search for criminals and terrorists among the crowd of thousands of spectators. Soon after that, facial recognition systems were installed in other sensitive parts of the US to keep track of felonious activities.
Although facial recognition is the fastest-growing biometric technology, it also happens to be the most controversial. After the 9/11 tragedy, many people supported the use of this new technology, but as the technology made deeper inroads to our lives, many realized that it could pose a threat to individual privacy and could also potentially lead to identity theft. No matter which side of this debate you’re on, it is worth knowing how this fast-growing technology works and what it can do.
How Facial Recognition Works
A facial recognition setup consists of advanced cameras that capture photos of people who pose or simply walk by, and sophisticated software working on those pictures will attempt to find the right match from the vast database to identify the person(s) in the image. Now, let’s take a closer look at the technical details of how these systems work.
As mentioned earlier, facial recognition methods vary slightly, depending on the application and manufacturer, but they generally involve a series of steps that serve to capture, process, analyze and match the captured face to a database of recorded images. These basic steps are:
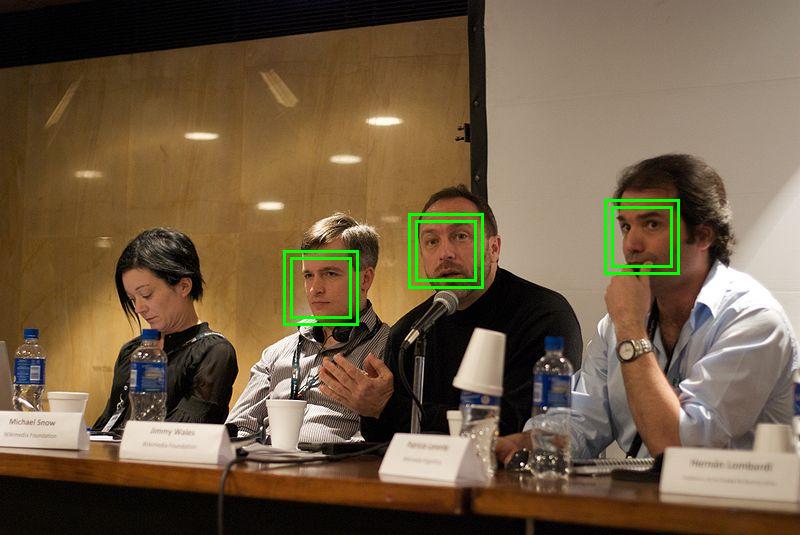
1. Detection:
When the facial recognition system is attached to a video surveillance system, the recognition software scans the field of view of the camera for what it detects as faces. Upon the detection of each face-like image on a head-shaped form, it sends the face to the system to process it further. The system then estimates the head’s position, orientation, and size. Generally, a face needs to be turned at least 35 degrees toward the camera for the camera to detect it.

2. Normalization:
The image of the captured face is scaled and rotated so that it can be registered and mapped into an appropriate pose and size. This is called normalization. After normalization, the software reads the geometry of the face by determining key factors, include the distance between the eyes, the thickness of the lips, the distance between the chin and the forehead, and many others. Some advanced face recognition systems use hundreds of such factors. The result of this processing leads to the generation of what is called a facial signature.
3. Representation:
After forming the facial signature, the system converts it into a unique code. This coding facilitates easier computational comparison of the newly acquired facial data to stored databases of previously recorded facial data.
4. Matching:
This is the final stage in which newly acquired facial data is compared to the stored data; if it matches with one of the images in the database, the software returns the details of the matched face and notifies the end user.
Applications Of Facial Recognition
National Security
A lot of organizations and businesses are using facial recognition, albeit for varying purposes. Governments across the globe are using facial recognition systems at airports to monitor people coming and going from their country. The US Department of Homeland Security, for instance, has a system to identify people who have overstayed their visas or may be under criminal investigation.
Apple iPhone
Apple’s iPhone first made facial recognition a household term. Since then, most mid-range to high-end smartphones come with a face unlock feature to authenticate the phone. Face unlock is a form of facial recognition that ensures that you are actually you when attempting to access your phone. Apple Face ID is arguably the most robust facial recognition feature out there when it comes to smartphones, with the chance of a random face unlocking the iPhone being just one in 1 million.

Most popular social media companies these days use some form of facial recognition. Facebook uses an algorithm called DeepFace to detect faces when you upload a photo to its platform. Upon uploading the photos, it asks if you want to tag people in the uploaded photos. If you allow this, it automatically detects faces and creates a link to their profiles. Facebook claims that its facial recognition system is 98% accurate.
Churches!
Interestingly, even some religious groups have started to use facial recognition technology to test the belief of their followers! Many churches are using a facial recognition system called Churchix to scan congregations and record the attendance of the individuals who are present. Facial recognition is helping church management keep track of people regarding the regularity of their church visits.
References (click to expand)
- Commercial Uses, Privacy Issues, and Applicable Federal Law. The U.S. Government Accountability Office
- DHS/USSS/PIA-024 Facial Recognition Pilot. The United States Department of Homeland Security
- Biometrics and Law Enforcement:. New York University
- Face recognition technology may threaten privacy | Bioethics Research Library - bioethics.georgetown.edu
- The global facial recognition market is expected to grow from .... PR Newswire













