Table of Contents (click to expand)
The build-up of dust can negatively impact your computer’s performance in 2 main ways: it causes the components of your computer to retain heat and it makes it more difficult for the internal fans to dissipate heat from the system, thereby decreasing the efficiency of the entire system.
My computer became very slow a few months ago, despite my attempts to fix it using software solutions like freeing up disk space, removing heavy programs, and defragmenting the drive. When I finally opened the computer cabinet, I found it covered in dust, which was the root cause of the problem.
Computers accumulate dust over time, so it’s worth checking for dust buildup if you’ve been using your computer for a while.
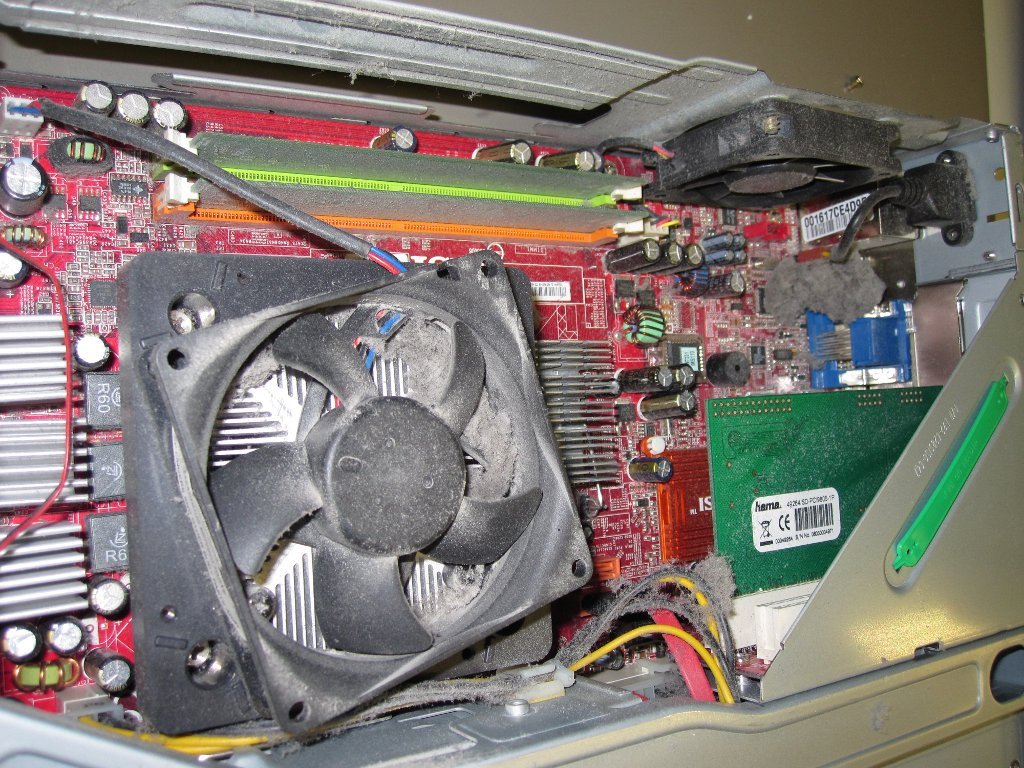

The build-up of dust is rarely considered a good thing in any context. When it comes to computers and similar electronics, dust deposition impacts the system’s performance in inconspicuous but potentially serious ways.
Recommended Video for you:
Computers And Heat
Computers are made up of electrical circuits and components that constantly produce heat as a byproduct of their processing. However, excessive heat output can cause problems and hinder the smooth functioning of the circuits.
Electronic engineers and designers constantly explore solutions to minimize heat dissipation to achieve superior computing and performance.

Even when left idle, computers still produce heat due to their steady-state power usage. While a small amount of heat output is normal, problems arise when the computer generates more heat than it can dissipate.
According to many computer repair technicians, dust accumulation is one of the most significant contributors to unregulated heating in a computer system.
Dust Buildup Hampers Airflow Inside The Computer Cabinet
As previously mentioned, the more a computer works, the hotter it becomes. For example, playing a high-graphics game on your computer puts more pressure on it than usual, producing more heat.
Like most things in life, too much of anything can have negative consequences. This is also true for modern-day computers. Too much heat can adversely affect the working capacity of various computer components.
Dust accumulation can have two significant negative impacts on your computer’s performance.
Firstly, it can cause your computer’s components to retain heat. Secondly, it can make it difficult for internal fans to dissipate heat from the system, reducing its overall efficiency.
Processor Throttling
Also referred to as frequency scaling, processor throttling slows down a computer (specifically, its processor) to use less power and avoid overheating. As we mentioned earlier, dust is the chief contributor to overheating.
Dust comprises many things, from dead skin cells, insect droppings, cigarette smoke, and any other junk that randomly floats around your house. Dust, dirt, and debris continually accrue inside the computer’s cabinet.
The problem worsens when this dust accumulates thickly near the fan and the heat sink. This impedes the fan’s speed and, thereby, its ability to quickly cool down the components inside.
When excessive dust builds up, vents get clogged, and the cooling fans have to work extra hard to maintain a safe temperature within the cabinet. The same thing is true with dust around the heat sink, which makes heat dissipation slower, causing the system’s temperature to rise quickly.
When the temperature rise goes beyond a certain threshold, the system moves into a processor throttling mode, wherein it slows down the computer in a bid to draw less power and thereby dissipate less heat. This translates into lag and slower processing speed for the end user of the computer.
Need For Processor Throttling
You may ask, why do computers do processor throttling? Well, the computer components are designed to work optimally up to a certain temperature. When the temperature rises dangerously to even higher levels, these components need to overwork, which can cause faster wear and tear, thus reducing the lifespan of the components. Also, if temperature is not controlled, some components may get damaged, which can cause further complications. For example, your computer may not even boot up!

Be Wary Smokers
If you are a serial smoker who smokes near your PC, you’re increasing the risk of hampering the performance of your PC even further. This is because any nicotine-laced smoke residue that gets inside the PC’s cabinet is quite acidic. It can corrode the pins and contacts much more quickly than other types of household dust.
Frequent Cleaning Helps Fix The Problem
To make sure that all of your computer’s systems run efficiently, it’s recommended that you open your computer cabinet (you can get a professional to do it, or even do it yourself, as it’s fairly simple) at least once every few months and clean the internal components, especially those parts directly on the motherboard. Professionals generally keep microfiber cloth, paintbrushes, dust busters, canned air, and isopropyl alcohol handy while doing the cleaning and you should do the same. Here are some quick tips and precautions you should take while cleaning up the computer by yourself.
Vacuuming
If you are cleaning your computer for the first time, it’s better to vacuum dust and debris away before opening the cabinet. Although professionals do vacuum after opening the cabinet, you’ll need to be very careful when doing so. This is primarily because vacuuming a high-power CPU can unsettle or dislodge computer components. Thus, if you’re a rookie who is cleaning your computer for the first time, you better do your vacuuming before loosening the screws of the computer cabinet.
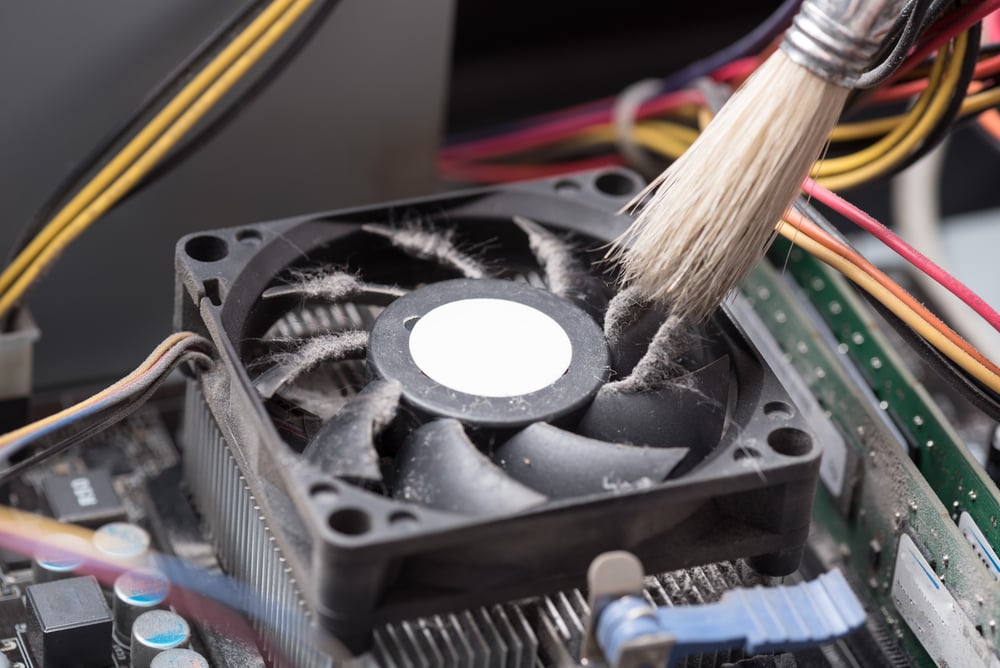
Brushwork
After opening the cabinet, reseat all the power and data cables on the drive. Ensure the computer is drawing no power from the mains or elsewhere. Now, wipe off the dust using a small brush and microfiber cloth, especially those areas near the fan and vents. Next, you can unplug the add-in card, which could be a sound or graphic card.

Reseating Cards
It is recommended that the cards be unplugged to clean out any dust that may have gathered beneath them. This helps with cleaning and counteracts something called “chip walk” or “chip creep.” This happens because a computer that runs with a high load heats up quickly, causing the components to expand slightly.
When the system is shut down, the temperature decreases, and the components contract. Over time, this cyclical expansion and contraction can cause the mounted cards to move out of place. Therefore, reseating the cards and manually inserting them again helps restore the key connections.
Canned Air Blast
After reseating the cards, you can use canned air to blow away the dust. However, if your cabinet is particularly dusty, the dust will fly as you shoot the canned air. For this reason, it is generally better to use canned air outdoors if the cabinet is very dusty. Use short bursts of air for optimal results.
Additionally, be cautious while using compressed air around the processor, memory, and card slots. You should do this from a few inches away since they are delicate but critical parts of a computer system.
Vacuuming, brushing, and a few shots of canned air can help you eliminate most of the dust inside your PC. You can use a microfiber cloth to wipe off any remaining stubborn dust. However, avoid using paper towels for wiping, as they tend to leave behind small fibers and dust on textured surfaces. Compared to paper towels, microfiber cloth barely leaves anything behind.
Cleaning all the dust and dirt may seem unpleasant initially, but if you do this regularly, you will likely witness a significant improvement in your computer’s performance and stability. The time you invest in cleaning your computer is undoubtedly worth the performance improvement it offers.
Last Updated By: Ashish Tiwari
References (click to expand)
- Why does electrical current make heat?.
- Leite, N. G. C., Reis, L. C. B. S., & Machado, H. A. (2021, September 21). Theoretical–experimental study of commercial heat sinks for personal computers. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering. Springer Science and Business Media LLC.
- Computer Hardware.
- Nabi, A., Rodgers, P., & Bar-Cohen, A. (n.d.). Prediction of thermal performance degradation of air-cooled fine-pitch fin array heat sinks due to fouling. Twenty-Second Annual IEEE Semiconductor Thermal Measurement And Management Symposium. IEEE.
- Kondo, M., & Nakamura, H. (2005). Dynamic Processor Throttling for Power Efficient Computations. Power-Aware Computer Systems. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.