Table of Contents (click to expand)
Plants excrete through stomatal pores on their leaves. The major metabolic reactions occurring in a plant that produce this waste are cellular respiration and photosynthesis. These processes are responsible for most of the gaseous waste produced by a plant. However, stomatal pores are not the only opening plants excrete through. This is because other than gases plants also excrete solid or gooey things.
If you were to cut through the layers and peek inside a plant, you would find a highly functional molecular industry inside.
Its resilient workers toil interminably to deliver chemical reactants on conveyor belts and single-wheeled carts, perpetuating a myriad of chemical reactions. The factory is constructed and run by Nature with a single aim: to keep it alive.
Furthermore, plants are not simply a mixed bag of chemicals that are spilled and exchanged randomly, nor do they work incoherently. Because they are exceedingly complex, Nature has divided the labor into teams. One of these methodical systems that remove the waste that accumulates throughout the body is the excretory system.
Excretion is one of the most important life processes that help to regulate life. However, animals are more biologically complex than plants, which is why a plant’s excretion system is much simpler and, consequently, more inept. Demands on a plant’s molecular machines are less taxing than they are on an animal.
The numerous metabolic reactions underlying these processes produce useful products, as well as unwanted toxins. When accumulated, these toxins can be fatal. An excretory system gets rid of these toxins or metabolic waste to ensure a longer, healthier life.
Recommended Video for you:
How Do Plants Excrete?
Like I said, plants lack complex machinery. Plants excrete through stomatal pores on their leaves. The major metabolic reactions occurring in a plant that produce this waste are cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
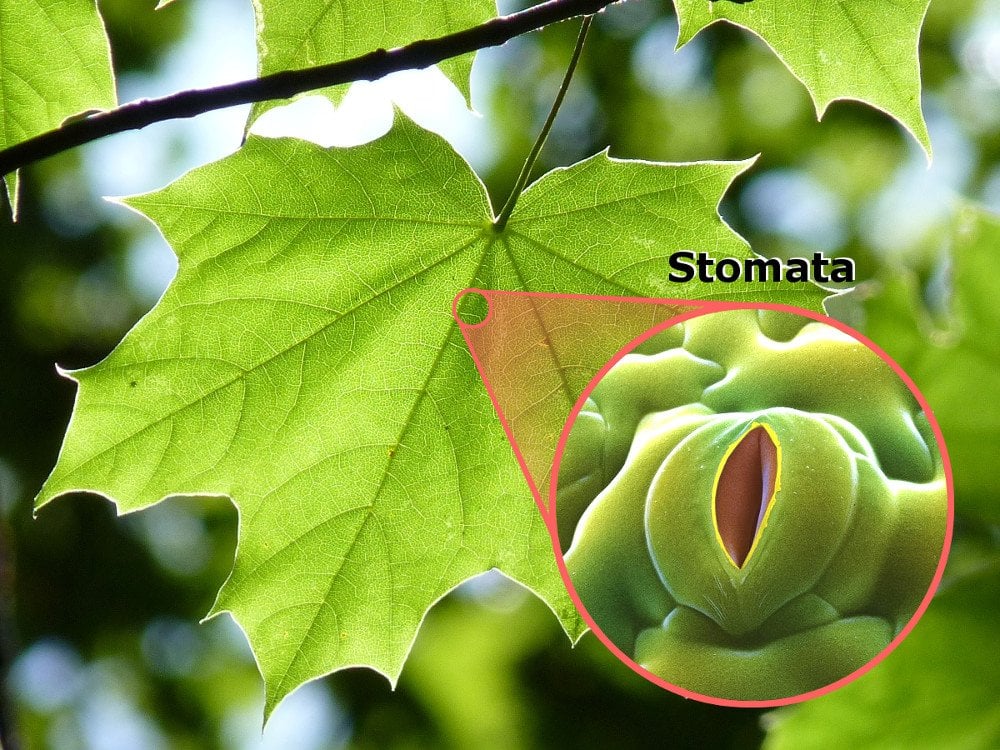
These processes are responsible for most of the gaseous waste produced by a plant. However, as we’ll find out, stomatal pores are not the only opening plants excrete through. This is because other than gases plants also excrete solid or gooey things.
Photosynthesis
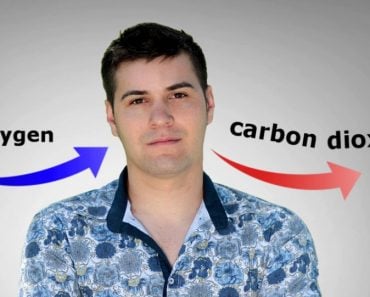
Photosynthesis is the process by which a plant forms simple sugar in the presence of sunlight. A plant converts light energy into chemical energy, which is utilized later to fuel its metabolic reactions. A reaction between water and carbon dioxide produces sugar and oxygen molecules.
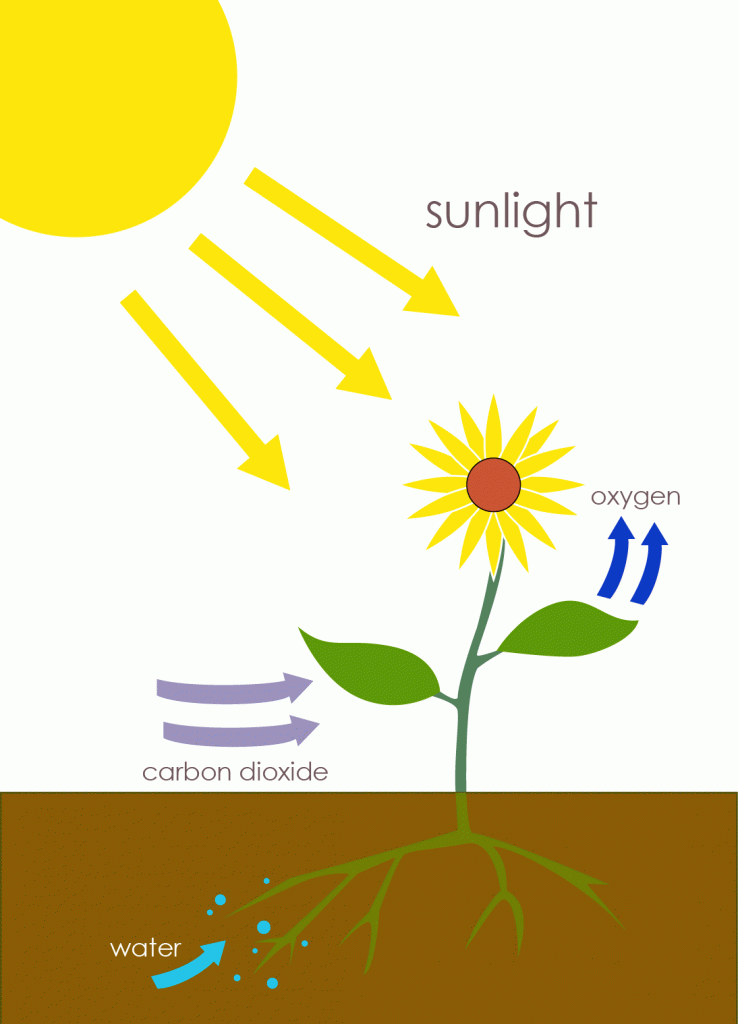
Along with melting of water, photosynthesis has to be the most consequential processes for the introduction and continuation of life forms. This is how plants provide us the air that we inhale – by breathing in the very air we exhale.
However, for them, oxygen is an undesirable toxin. The oxygen is released through pores into the surrounding air.
Respiration
Plants respire just like every organism does. Respiration is the process by which a plant converts the energy stored in the form of glucose or “food” into resourceful chemical energy. This process is essential for providing the “workers” with the energy to carry out metabolic reactions.
The gaseous waste produced when a plant cell respires is carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide oozes through its pores and is simultaneously used as the reactant for photosynthesis. Similarly, the oxygen produced by photosynthesis is utilized for cellular respiration.

Plants obtain a voluminous quantity of carbon dioxide from animals, and in return, plants replenish us with oxygen. In this way, plants and animals share a symbiotic relationship. They live and benefit from each other. The absence of one would fatally affect the survival of the other.
Transpiration And Other Excreta
Plants also excrete nitrogenous compounds that are produced in protein metabolic reactions. Another method is transpiration, whereby plants excrete excess water through their leaves, which are suffused with stomatal pores, or they cause this water to profuse from fruits and stems.

Metabolic reactions also produce organic “waste”, which assumes different shapes and occupies different parts. These include gums, various oils, latex, resins and a multitude of crucial products that we borrow from plants. These substances are found on barks, succulent stems and colorful leaves.