Table of Contents (click to expand)
Darkness can’t possibly be faster or slower than light, since darkness possesses no physical properties of its own.
What do you see when you look up at the sky?
Emptiness.
Well, not exactly emptiness, but an expanse so vast that anything it contains seems like a mere speck of dust in the open sky. During the day, this vast expanse seems light blue to anyone on the surface of the Earth. This is due to the scattering of the Sun’s light rays in Earth’s atmosphere. However, when the Sun sets, and there is no external source of light, we see the true colors of the Universe, the true color of the Universe being no color at all. That’s why we refer to it as space. Being an empty, open space leaves it in darkness.

To the human eye, darkness and light are two opposing entities, so from a scientific standpoint, which one of them is faster? Which one would traverse the distance from point A to point B quicker? The short answer to this question is that there is no comparison to be made, as darkness does not possess a speed of its own. However, this short answer isn’t exactly a satisfying answer. For that, we need to understand the relationship between light and darkness.
Recommended Video for you:
Are Darkness And Light Two Opposing Entities?
When we look up at the night sky, the shining lights of the stars stand out against the darkness of the Universe. So, if they look like polar opposites to the human eye, and we consider them as opposites in all aspects, be it media, art, good and bad, Yin and Yang, they must actually be opposing entities, right?
Wrong.
Now, light travels at a rough speed of 300,000 kilometers per second in a vacuum (in the absence of a medium). That is, light possesses speed of its own and, therefore, physical properties of its own. Furthermore, we can produce light because light has a source from which it originates. This makes light an independent physical entity.

However, the same principle doesn’t apply to darkness.
Darkness does not possess a speed of its own. We cannot create darkness, as darkness has no source. In fact, the only reason why humans can identify darkness is that light exists. Scientifically, darkness is not an independent physical entity. Darkness is defined as merely the absence of light. It is mere emptiness.
96% of the universe that humans have observed is darkness. It is either nothing, or it is full of objects so far away from Earth that their light hasn’t reached our field of vision yet.
Look at it this way: Why do we experience day and night on Earth? Why do other planets that don’t possess an atmosphere not experience the phenomenon of day and night?
This is because the Sun’s light gets scattered and trapped by the Earth’s atmosphere while we are facing the Sun for however many hours a day. The amount of time it takes for night to turn into day depends on the amount of time it takes for the Sun, i.e., the Earth’s light source, to be completely hidden from view at night, until it pops back into our view in the morning.
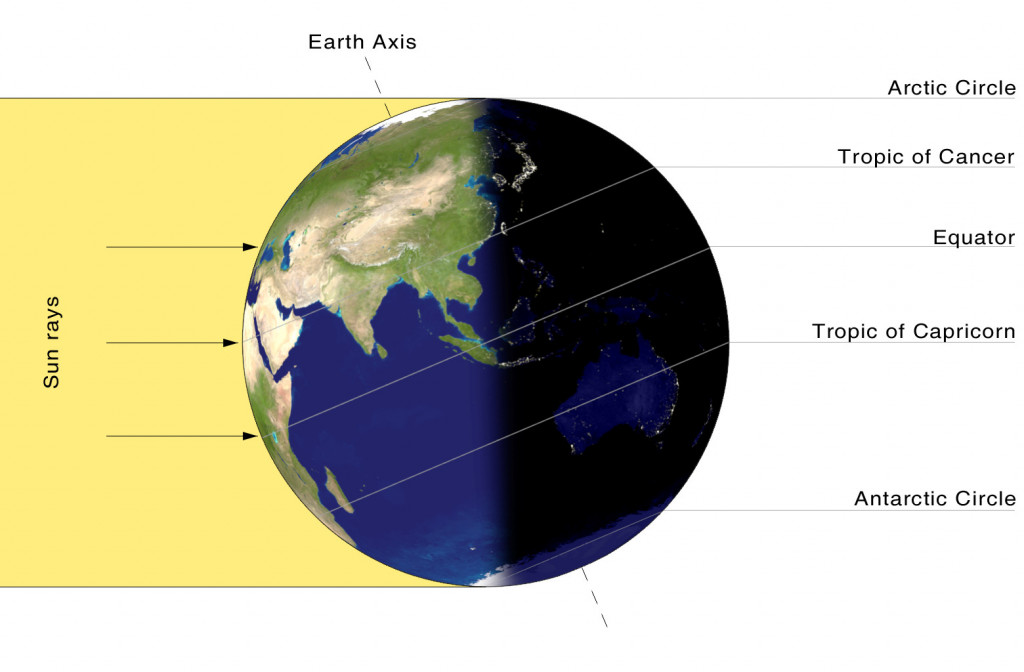
Darkness, once again, has no source, so the amount of time it takes for day to turn into night also depends on the light source itself. Therefore, we once again arrive at the conclusion that darkness possesses no speed of its own. Since darkness is defined as the absence of light, its speed is the same as that of light. Therefore, the speed of darkness is also 300,000 kilometers per second.
Light Or Darkness: Which Is Faster?
To present this from a purely scientific point of view: To find out whether darkness is faster or slower than light, we would need to compare their speeds. Speed here is not relative. For either of these to be deemed quicker or slower, both must possess their own speed. Now, light in a vacuum possesses a speed of 300,000 kilometers per second. This speed changes from medium to medium, being 225,000 kilometers per second in water, 200,000 in glass[2], etc.
Darkness, on the other hand, possesses no speed of its own.
So, scientifically, no comparison can be made, since darkness cannot be produced, and no speed can be ascertained. The speed of darkness in an environment where light is present can only be calculated at a point where light is receding, so the speed of darkness would be the same speed at which the light is moving.
Therefore, the speed of darkness would also be 300,000 kilometers per second in a vacuum, 225,000 kilometers per second in water, and so on. From a scientific standpoint, darkness is neither faster nor slower than light, since it travels at the speed of light itself.
References (click to expand)
- The Dark Universe - Chandra X-ray Observatory. The Chandra X-ray Observatory
- Speed of Light in Transparent Materials - Molecular Expressions. Florida State University
- Jo, B., Kim, H., Kim, H. D., & Shin, C. S. (2021, April 27). Exploring the Universe with dark light scalars. Physical Review D. American Physical Society (APS).