Table of Contents (click to expand)
The idea of residing within a hologram remains a hypothesis. It has not been universally accepted among physicists and continues to be one of several theories attempting to elucidate the fundamental nature of our universe.
Imagine, for a moment, that our entire existence is nothing more than a hologram—a three-dimensional image projected onto a two-dimensional surface. It’s an idea that may sound a lot like science fiction, but in the world of physics, it’s a concept that has been quite seriously explored. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of living within a holographic universe, unraveling its mysteries, and shedding light on the intriguing nature of our existence.
Recommended Video for you:
What Is A Hologram?
Let’s start with the basics. You might have seen holographic stickers on your credit card. These stickers do something pretty amazing—they create 3D images that seem to pop out when you look at them from different angles. But how do they do that?

Holograms work by capturing how light interacts with an object and then using that information to create a lifelike 3D image. It’s like taking a snapshot of how light bounces off an object and then turning that snapshot into a 3D scene.
Interference: The Secret Behind Holograms
Now, here’s where the magic really happens. To make a hologram, we use something called “interference.” Don’t worry, it’s not as complicated as it sounds. Think about it like this: when you drop a pebble into a pond, it creates ripples in the water. `Where the ripples overlap, you see patterns of light and dark areas.

Holograms work in a similar way. We use a special kind of light (from a laser) to create patterns of light and dark areas on a special surface. These patterns hold all the important information about the object we want to capture. It’s like a secret code that turns into a 3D picture when we decode it.
The Holographic Principle
The intriguing notion that our universe might be a hologram is rooted in a concept known as the ‘Holographic Principle.’ This principle, which first gained attention in the late 1990s, was initially proposed by physicists Leonard Susskind and Gerard ‘t Hooft, with major contributions to its development from string theorist Juan Maldacena.
According to this principle, all the information about the events occurring within a particular space can be encoded on the boundary of that space, much like a 2D hologram encapsulates the information of a 3D object. This concept carries profound implications for our understanding of the fundamental nature of the universe.
The essence of this principle lies in its suggestion that everything taking place within a defined region of space can be represented in terms of the information stored on its boundary, rather than the volumetric space within it. It’s akin to envisioning a cosmic data storage system where the boundary contains all the essential data, and the interior space merely acts as a projection of that data.
The Black Hole Connection
Now, you might be wondering how this seemingly abstract concept connects to our everyday reality. This is where the enigmatic celestial entities known as black holes enter the scene. Black holes are incredibly dense regions in space, characterized by such intense gravitational forces that not even light can escape their clutches.
Scientists have proposed a rather mind-boggling idea, suggesting that all the information regarding objects that venture into a black hole could be encoded on its event horizon—the boundary encircling the black hole. In essence, this boundary could serve as a cosmic hologram that retains a record of everything that has been drawn into the black hole’s gravitational grip.
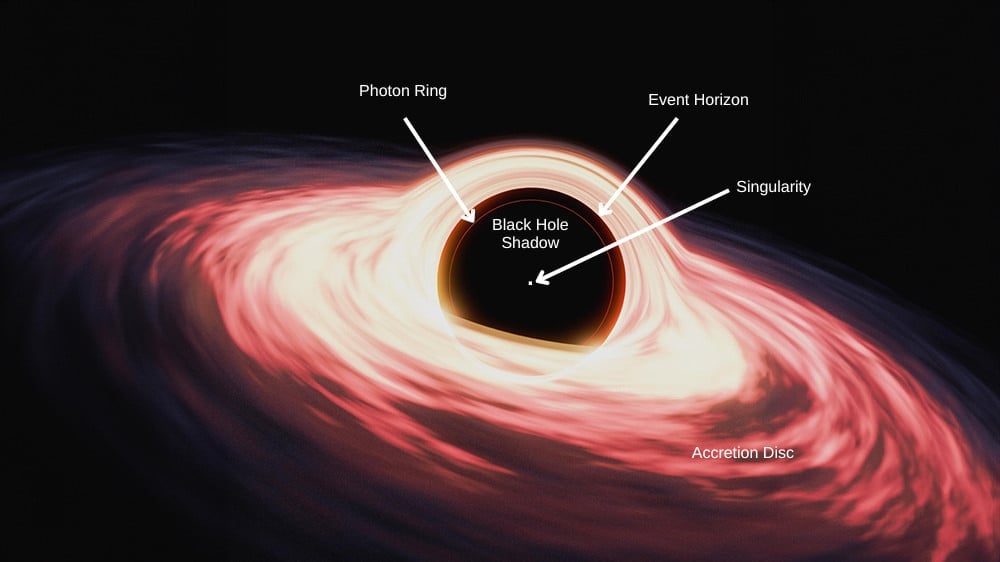
To provide some context to this concept, let’s draw an analogy with the experience of watching a movie in a traditional cinema. As you sit in your theater seat, engrossed in a 3D film, you may feel as though you’re an integral part of the action unfolding on the screen. However, the reality is that the entire movie is essentially a projection on a flat screen.
Similarly, the Holographic Principle proposes that our familiar 3D universe might be a universal-scale projection of information encoded on a 2D surface—a sort of “screen” for our reality. This analogy offers a simplified visualization of how our 3D perception of the world could potentially emerge from information contained on a lower-dimensional surface.
Why Does It Matter?
The concept of living in a hologram remains a subject of ongoing scientific discussion and exploration. It has certainly not yet transitioned from the realm of theory to established fact. Nevertheless, its significance lies in the profound challenges it poses to our understanding of the universe.
By exploring this concept, scientists aim to establish connections between diverse branches of physics, bridging the realms of quantum mechanics and general relativity.
This idea presents a promising solution to some of the prominent conflicts in modern physics. For instance, it offers a potential means of reconciling the seemingly contradictory laws of the quantum world with the principles governing the universe on cosmological scales. In the realm of quantum mechanics, the phenomenon of superposition allows particles to exist in multiple states simultaneously.
The holographic universe concept offers an intriguing framework for understanding how superposition functions, as well as its influence on our perception of reality.

Moreover, this perspective has the potential to close the gap between Einstein’s theory of general relativity and quantum mechanics—two extraordinarily successful theories in their respective domains. The holographic principle provides a unique framework for harmonizing these seemingly conflicting descriptions of the universe.
In essence, the idea of living in a hologram serves as a powerful thought experiment that pushes the boundaries of our comprehension of reality. While it may initially sound far-fetched, it serves as a vivid reminder that the universe is teeming with mysteries waiting to be unraveled, and our perception of reality may be far more intricate (or limited) than we have dared to imagine.
Ongoing Research And Questions
The concept of a holographic universe continues to be an active area of research and speculation within the realm of physics. Scientists are actively engaged in experiments and mathematical modeling to assess the validity of this concept.
One particularly intriguing facet of this research pertains to the study of cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), which represents the afterglow of the Big Bang. By examining the patterns and irregularities present in the CMB, researchers aspire to uncover evidence that supports the holographic principle. These patterns may serve as clues indicating the presence of information encoded on the boundary of our observable universe.

However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the idea of residing within a hologram remains a hypothesis. It has not been universally accepted among physicists and continues to be one of several theories striving to explain the fundamental nature of our universe.
A Final Word
The idea of living in a hologram is a concept that continues to captivate the imaginations of scientists and thinkers around the globe. While it may seem complicated at first, we can comprehend it by contemplating how 3D images can be projected from 2D surfaces, much like the holograms we encounter in everyday life.
Whether we truly exist within a hologram or not remains an enigma that scientists are diligently working to solve. This concept challenges our comprehension of the universe and raises profound questions concerning the nature of reality. As we venture deeper into the realms of physics and cosmology, we may discover that the answers to these questions are more mind-bending than we could have ever envisioned.
Ultimately, the pursuit of knowledge is a thrilling journey, and concepts like the holographic universe serve as poignant reminders that the universe is replete with wonders yet to be uncovered and mysteries waiting to be unraveled. In our quest to understand the nature of reality, we continue to find that the universe is full of captivating and mind-expanding possibilities.