Table of Contents (click to expand)
Planets rotate because when they form from a collapsing cloud of gas and dust, the rotation of the cloud is conserved. This is why all planets rotate in the same direction.
After spending a handful of years as children, we go on to become teenagers. After spending a few miraculously brief years in the teenage era, we become adults, and ultimately, we enter the age when people start to address us as ‘senior citizens’. Throughout all these years, we hear hundreds of thousands of facts and claims; some are questioned, but many of the others are allowed to sink into our minds for all eternity.
One such thing that most of us are aware of is the fact that planets rotate. Every planet in the solar system rotates; it’s one of those undeniable truths of the universe that is accepted by one and all, but have you ever questioned it? More specifically, have you ever wondered why planets rotate?
Recommended Video for you:
Momentum
Before delving into the world of celestial bodies, let’s briefly unpack this simple yet fascinating concept of physics.

To put it in simple terms, momentum is ‘mass in motion’, or the ‘quantity’ of motion that a body possesses. If an object has mass and is moving, then it has momentum, which means that it’s going to take a certain amount of effort to make it stop. You have likely heard the word ‘momentum’ many times in sports; if a football team has won a few games in a row, then it is said to have some ‘positive momentum’, meaning that it will require considerable effort from its opponents to hand the team a loss.
In scientific terms, when an object (having mass ‘m’) moves with a velocity ‘v’, then it has a momentum with a magnitude of ‘mv’ (the product of ‘m’ and ‘v’).
Angular Momentum
Much like momentum, angular momentum is the ‘quantity of motion’ that a body gathers when it undergoes a rotary motion or moves around an axis that may or may not pass through the object itself. There are many examples of angular momentum around you, such as a quarterback imparting a spin while throwing the ball, a bullet spinning as it leaves the muzzle of a gun and so on.

And yes, in reference to the title of this article, planets also rotate due to angular momentum.
Conservation Of Angular Momentum

In technical terms, the principle of conservation of angular momentum states that, “If no net external torque acts on a system, then the total angular momentum of the system remains constant.”
In the absence of an external force, if two objects interact with another (say, two rubber balls colliding with each other), then the total angular momentum of the system of these two bodies remains conserved. It means that there is no net loss of angular momentum after the interaction.
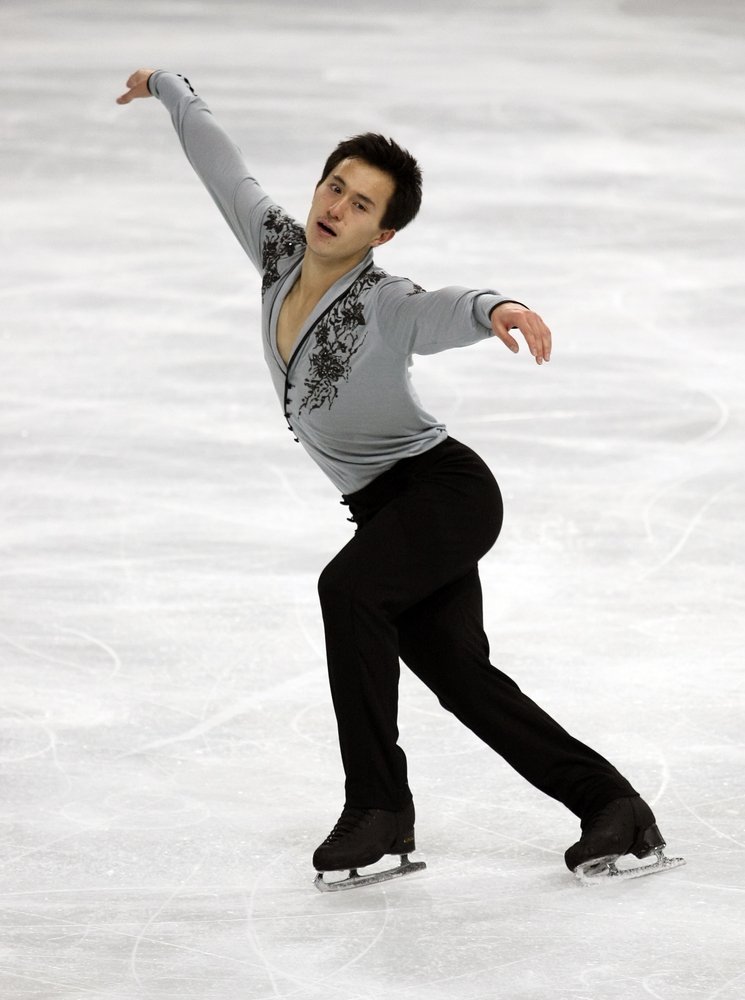

A great example of conservation of angular momentum is the spinning motion of ice skaters; have you wondered how they seem to effortlessly alter their rotating speeds? They stretch out their arms and legs to slow their spin, but as soon as they bring their limbs close to their body (in line with the rest of the body, which is their axis of rotation), then they spin very fast.
This principle applies directly to the rotation of planets.
Where Does Planetary Rotation Fit In The Picture?
It has do with the time when stars and planets are formed. They form due to the collapse of humongous clouds of gas and dust. The materials present in the clouds, and the clouds themselves, were in motion due to the aggregate gravity of the galaxy. So, when seen from the center of the clouds, it would appear that the cloud is in a spinning motion.
When a cloud collapses, however, all of its components also collapse independently and break down into small pieces (when we say ‘small pieces’, consider these in terms of hundreds of miles in size; come on, we’re talking about the universe here!). Each of these fragments contains some part of the angular momentum of the parent cloud. Eventually, these rotating clouds flatten themselves to become protostellar disks (protostellar disks are gas clouds around a forming star that are flattened by rotation). It is from these disks that planets and stars are born.

Through a process that is not fully understood yet, the particles in the accretion disk (a rotating disc of matter formed by accretion around a massive body under the influence of gravitation), each of which has their own angular momentum, combine together and a planet is formed!
This is the reason why every planet in the universe, that we know of, rotates. It’s also interesting to note that except for Venus and Uranus, all the planets in our solar system rotate from west to east.
You should be proud of yourself! Now you know the reason behind one of the most common, yet most intriguing behaviors, of planets – their common feature of rotation!
References (click to expand)
- Why is Earth rotating? Did it always have the same rotation period? Will it always have the same rotation period? - spaceplace.nasa.gov
- Why do planets rotate? (Intermediate) - Curious About Astronomy .... Cornell University
- Why and how do planets rotate? - Scientific American. Scientific American
- The Direction of the Rotation of Planets - www.sjsu.edu