Table of Contents (click to expand)
Yes, metals can be gases, depending on how high their boiling points are… but are gaseous metals really considered metals?
Close your eyes for a moment and let the word ‘metal’ float around in your head. So, what’s the first image that comes to your mind when you think of ‘metal’?
Some of you may see something like this:

But I think most of you will envision a hard, shiny solid object—maybe a shiny sword, a slick car or clean cookware?
We associate the word ‘metal’ with solid objects, as most metals around us are solids. But are metals restricted to the solid state? Can they be a gas?
Recommended Video for you:
Can A Metal Be A Gas?
Yes, absolutely! Although metals usually occur in a solid state at room temperature (which is probably why we associate the word ‘metal’ with solid objects), metals can be in a gaseous state.
The thing about states of matter is that they are universal: a metal can be solid, liquid or gas, but that state is decided based on the right conditions of temperature and pressure.
For instance, a metal, say, lead, has a boiling point of 1740 degrees Celsius. Now, you know that lead, in its ‘natural state, is a solid, but when you start heating it, it will first turn into a liquid at 327 degrees Celsius, and if you continue to supply more heat, it will turn into gas at 1740 degrees Celsius.

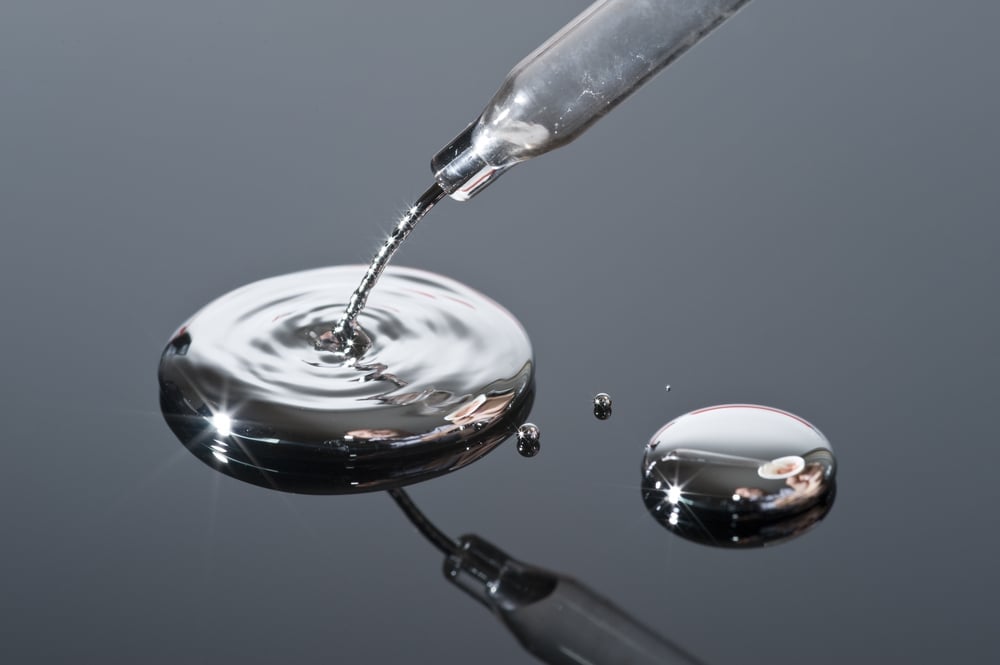
Another excellent example is mercury. In fact, it’s the metal with the lowest boiling point (356.7 °C), meaning that of all metals, it turns into gas at a relatively lower temperature.
However, it is important to note that mercury vapors are very harmful. According to the World Health Organization, “the inhalation of mercury vapor can produce harmful effects on the nervous, digestive and immune systems, lungs and kidneys, and may be fatal. The inorganic salts of mercury are corrosive to the skin, eyes and gastrointestinal tract, and may induce kidney toxicity if ingested” (Source).

Now, let’s discuss another aspect of this metal-to-gas saga.
Does A Metal Remain A Metal When It Turns Into Gas?
We’ve established that metals can turn into gases if they’re heated to their boiling points, but once a metal is heated to its boiling point and becomes gas, is it still metal? In other words, can a metal be in a gaseous state and still be considered a metal?
The short answer? No.
Gaseous metals don’t retain the properties of their solid counterparts, including the metallic bonds, metallic conductivity, ductility, luster or other metallic properties. This is why metals are no longer considered metals when they assume a gaseous state – they’re just gas with certain characteristic properties of the ‘parent’ element, i.e. “mercury gas”.
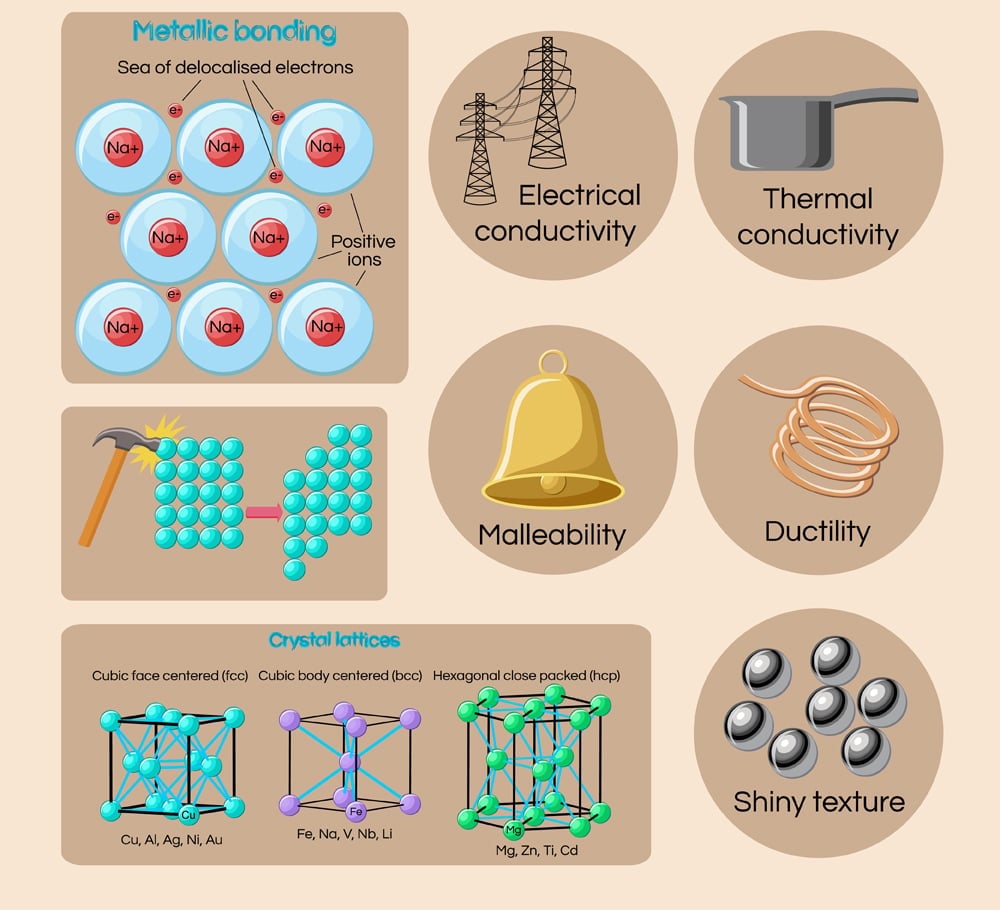
Why Are Metals Solid?
Metals are solid at room temperature because of how their consistent atoms are packed together.
You see, all matter is made of atoms. The state of a substance relies on how close or far apart these atoms are to each other.
If the constituent atoms of a substance are far apart, then that substance will exist as a gas at room temperature. Atoms in the liquid state are relatively closer together, but in solids, atoms are packed together in very tight crystals.
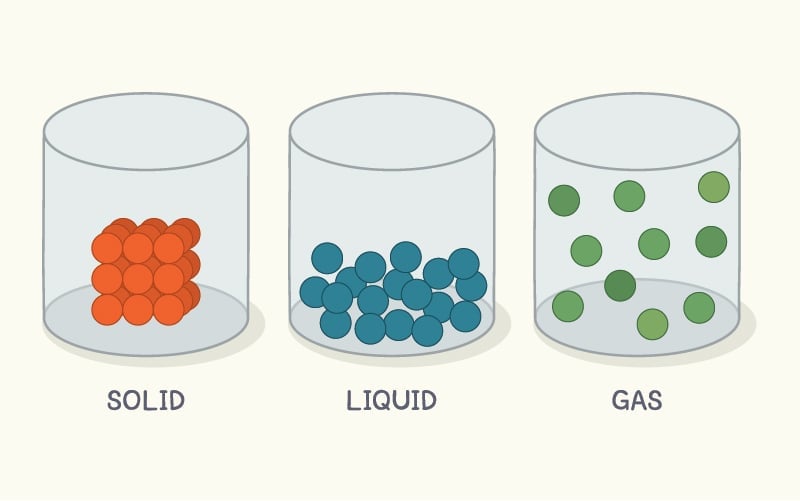
Due to the strong forces that hold these atoms close together, solids are rigid and have a definite shape and size (unlike liquid and gas).
Metals are solid at room temperature, due to the constituent atoms of metals being packed so close together, imparting them a rigid or ‘set’ exterior. This is also why metals have high melting points and don’t exist in a liquid state at room temperature.
All in all, metals can be converted into gas, but once they turn into gas, they don’t retain their metallic properties.