Table of Contents (click to expand)
Fulminated mercury is an unstable mercury salt of fulminic acid. The scene in Breaking Bad was only partially accurate; they got a few things right and a few things wrong.
Fulminated mercury or Mercury Fulminate is a pop culture favorite when it comes to a quickly improvised explosive that can be cooked in a lab or a basement. It has gained some screen time in shows like Breaking Bad, Law and Order and Burn Notice.
What Is Fulminated Mercury?
Mercury(II) Fulminate, as the name suggests is an ionic compound formed between mercury and fulminate ions. In Mercury (II) Fulminate, one unit of mercury ion (Hg2+, hence the II after mercury) combines with two units of fulminate ions (CNO–).

The -1 charge (due to an excess electron) on each of the two CNO– units compensate for Hg’s loss of two electrons (the +2 charge on Hg). As a result, they form a neutral, but very explosive compound with the chemical formula (Hg(CNO)2).
Recommended Video for you:
The Fulminated Mercury Scene Of Breaking Bad
Was the Breaking Bad scene about fulminated mercury scientifically accurate?
The answer is: it was partly right.
Yes, a crystal of mercury fulminate would explode when slammed to the floor.
However, the crystal seen in Breaking Bad does not resemble mercury fulminate crystals. These are usually grey or light-brown due to the presence of colloidal mercury. Only an extra-pure crystal, synthesized in a professional laboratory, would look like the one in the show. It is unlikely that a crystal of this size could be grown as it is highly unstable and extremely sensitive to even the slightest vibrations or light.
Furthermore, in that particular episode, Walter White places the crystal in a bag and handles it roughly while taking it to the drug dealer. However, in reality, a crystal that size could never have survived past the point of it being placed in the bag. Even the slightest movement could have caused it to detonate.
So, yes, they did tweak the chemistry a little bit, but the dramatic visual outcome makes this slight fib completely worth it.
History Of Fulminates And Explosives
The chronicle of fulminated mercury dates back to the days of alchemy in the 17th century. Alchemists like Cornelius Drebbel and Johann Krunckel figured out that metals like silver or mercury, when mixed with spiritus vini (ethanol) and aqua fortis (nitric acid), gave rise to an explosive concoction.
During the later half of the 18th century, chemists mastered the art of making fulminating platinum, silver, and gold. Salts of these metals (carbonates or chlorides) were dissolved in ammonia. The precipitate obtained was then carefully dried (in the absence of heat or light). The resultant powder would explode at the slightest friction or heat.
The explosions felt almost like a thunderbolt. In fact, that is where the name fulminate was derived from, as fulmen in Latin means thunderbolt.
These powders were used as a source of entertainment and also as ammunition during war, especially fulminating gold. However, modern chemists have uncovered that what was called gold fulminate wasn’t actually a fulminate at all, as it doesn’t have the CNO– group. Instead, it is a complex salt that consists of ammonium (NH3+), nitrate (NO3–), and Chloride (Cl–) ions.
They also tried similar ammonia precipitation with mercury salts, but no one could isolate it. At least, that was true until the year 1800, when an Englishman named Edward Charles Howard became the first chemist to isolate it. He also presented a detailed method for the preparation of mercury fulminate (which by the way, he discovered accidentally).
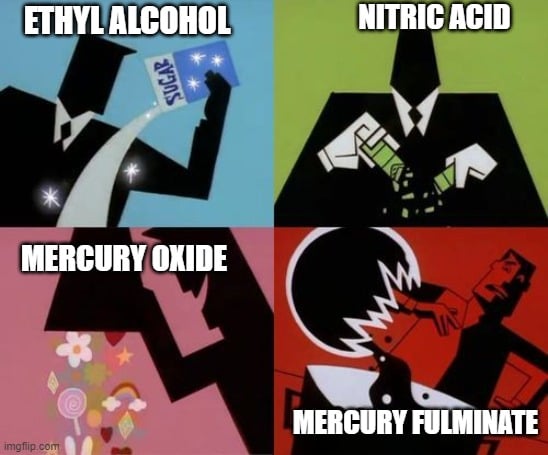
Edward was actually researching ways to synthesize muriatic acid (HCl). During his inquest, he realized that it contained hydrogen. To verify his newly acquired knowledge, he set up an experiment. To a mixture of ethyl alcohol and nitric acid, his hydrogen and oxygen sources, he added red mercury oxide as a second source of oxygen (they didn’t know that muriatic acid needed chlorine and not oxygen) and stirred them together.
All of a sudden, his reaction mixture began to bubble and release dense white smoke. After it calmed down, he could see a white precipitate settle at the bottom of his reaction container.
He crystallized the white precipitate and added a few drops of sulphuric acid to it. Initially, an effervescence was seen, followed by an explosion. He was so amazed by the explosive properties of these crystals that he tried to fulminate (detonate) them using different methods.
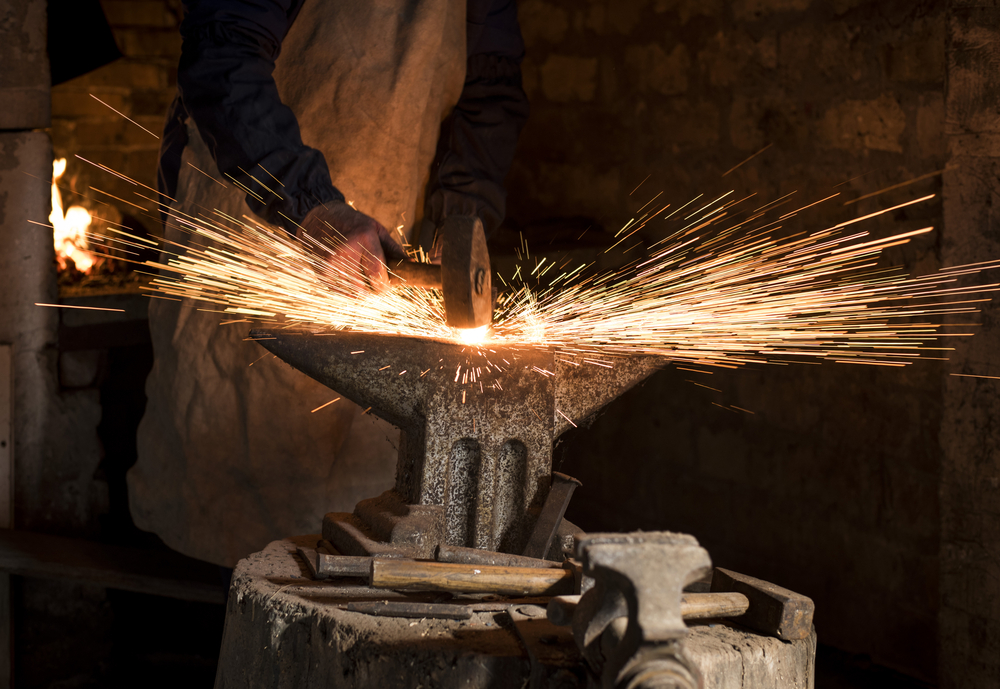
One such experiment involved placing a few crystals (3-4) of mercury fulminate on a cold anvil and then tapping it with a hammer. A slight tap not only resulted in an explosion, but also left behind dents on both the hammer and anvil (both of which are solid metal objects).

Edward’s curiosity wasn’t quenched by the simple experiments; he wanted to try something even bigger (and probably even more dangerous). With his friend John Abernethy’s help, he loaded a gun with 11 crystals of his invention, instead of gunpowder. When the trigger was pulled, it created an explosion so intense that it ruptured the gun itself.
After many more trials of igniting it with impact, heat, or electric spark, he concluded that the firepower of mercury fulminate was due to the spontaneity of combustion.
After being convinced that the substance he created was a potent explosive, he penned down a detailed procedure on how to obtain mercury fulminate (which I won’t detail here for safety reasons). He recommended producing only 500 grains in a batch to avoid major destruction due to any accidental combustion of the product. Even after all these years, commercial manufacturers of mercury fulminate still follow a process very similar to Edward Howard’s.
<h2>Structure Of <i>Mercury fulminate</i></h2>
The investigation into the structure of mercury fulminate began with the advent of X-ray crystallography. In the 1960s, scientists discovered that the compound was a mercury salt of fulminic acid (they share the same skeletal structure).
Almost two centuries after its discovery, the bonding arrangement, and the crystal structure, of mercury fulminate, was finally determined in 2007. A group of German researchers led by Wolfgang Beck and Thomas Klapötke used the X-Ray diffraction technique to put an end to the quest.
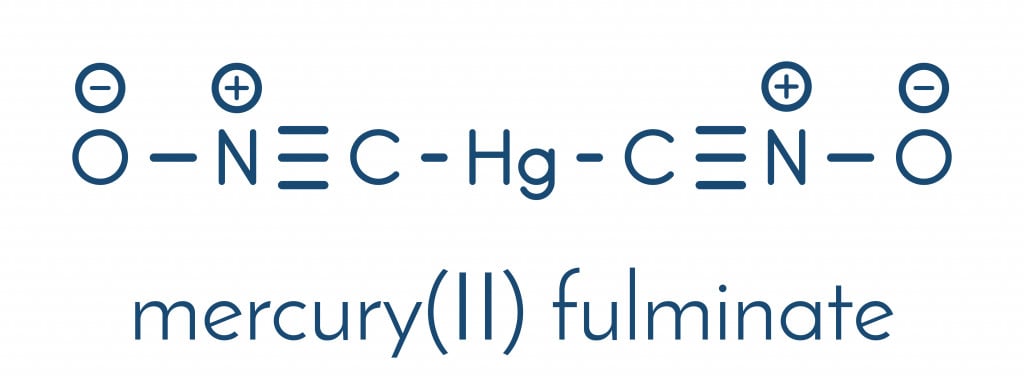

The secret behind its explosive nature lies in its structure. As you can see in the image above, both fulminic acid and mercury fulminate have the fulminate ion (CNO–), in which the carbon is attached to the nitrogen with a triple bond and the nitrogen, in turn, is attached to the oxygen atom via a single bond. This weak single bond between the N and O atoms is what makes fulminated mercury unstable and explosive.
Conclusion
Mercury fulminate ruled the world of explosives as a primary detonator for ammunition throughout many wars. Even Alfred Nobel used it in the blasting caps used to detonate dynamite.
Thus, Edward Howard’s accidental invention not only makes our crime thrillers look more theatrical, but is also indirectly the reason why Nobel Prizes exist!
References (click to expand)
- Wisniak, J. (2012, April). Edward Charles Howard. Explosives, meteorites, and sugar. Educación Química. Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico.
- Edward Charles Howard - Linda Hall Library. The Linda Hall Library
- (1800) On a New Fulminating Mercury. By Edward Howard ... - jstor. JSTOR
- Breaking Bad IV – can a little crystal blow up a room?.
- 300 years after discovery, structure of mercury fulminate ....












