Electric fires or battery pack fires occur due to thermal runaway, which stresses the battery pack, causing it to explode.
Batteries are a timeless marvel of chemistry and engineering. To be able to carry the power of Zeus in your pocket is no mean feat, and batteries enable us to do just that! With electric mobility on the rise, battery technology is only set to surge. However, batteries in scooters are still posing somewhat of a challenge. With EV fires dotting some parts of the globe, this issue demands an explanation.
Recommended Video for you:
Why Do Electric Scooters Sometimes Catch Fire?
Before you jump to conclusions, don’t let this generalized assertion scare you. Electric scooters and vehicles in general do not catch fire very often. The modern battery pack that powers electric vehicles has many safety features that prevent it from catching fire.
However, fires pose a real danger with some faulty battery packs, as has been observed in some regions. The reason for these fires is known as thermal runaway, in scientific parlance.
What Is Thermal Runaway?
Before we begin, let’s look at a common phenomenon that we have all experienced at some point. If your smartphone has a metallic body, you will feel it heating up after constant use. On the flip side, the metallic body will heat up even when the phone is being charged and not in use. So why do we draw parallels between EVs and smartphones?
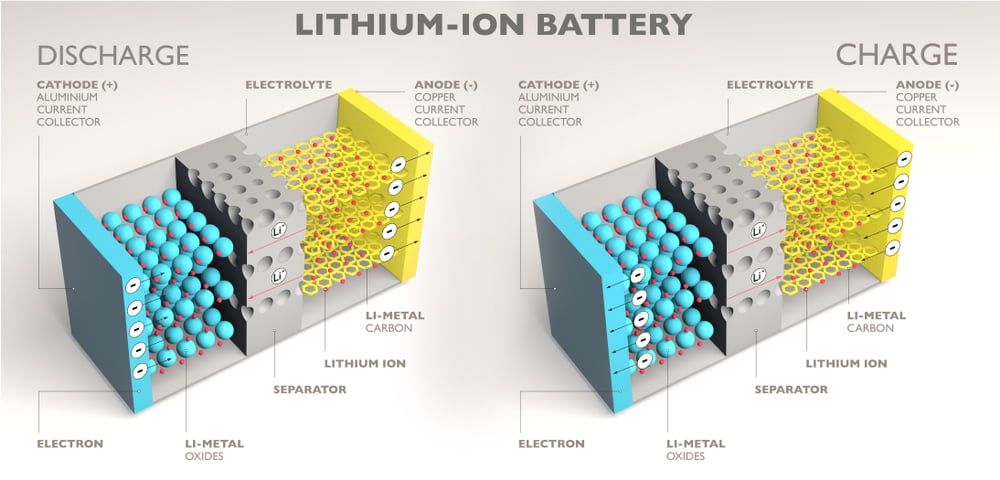
Most portable appliances today, including EVs and smartphones, are built around the lithium-ion battery. Amongst the most favorable characteristics of this battery include its compact construction, the absence of liquid electrolytes, and high energy density. That high energy density, however, is also its biggest disadvantage.
When a Li-ion cell is charged, an endothermic reaction takes place, due to which the system absorbs heat. On the other hand, the system releases heat during the cell’s discharge, as the chemical reaction is exothermic. If this heat is not removed from the system effectively, it results in an unstable system. An unstable cell starts a chain reaction, enveloping its neighboring cells in the battery, often resulting in explosions and fire. This is known as thermal runaway.
How Can Thermal Runaway Be Prevented?
In order to prevent thermal runaway in battery packs, it is important to reduce load on the system. Battery loading is not only restricted to abusive charging and discharging cycles. It also includes mechanical stresses, such as compression and vibration. The key to reducing the risk of thermal runaway therefore lies in robust battery management, along with appropriate heat dissipation and physical isolation of the battery pack.
Battery Management Systems
In order to prevent thermal runaway, battery packs are fitted with a battery management system that monitors each cell for irregular vital signs, such as a surge in temperatures.
In the event of something extraordinary, the BMS isolates the cell from the remaining battery pack and delivers reduced performance for the appliance. If the entire battery pack becomes unstable, the BMS triggers a cutoff to prevent it from overloading.
Heat Dissipation In Battery Packs
Heat dissipation in battery packs can be done in a few ways that are very similar to those used in internal combustion engines. The first is using air cooling, where the battery pack relies on vehicular motion to come into contact with cool ambient air.
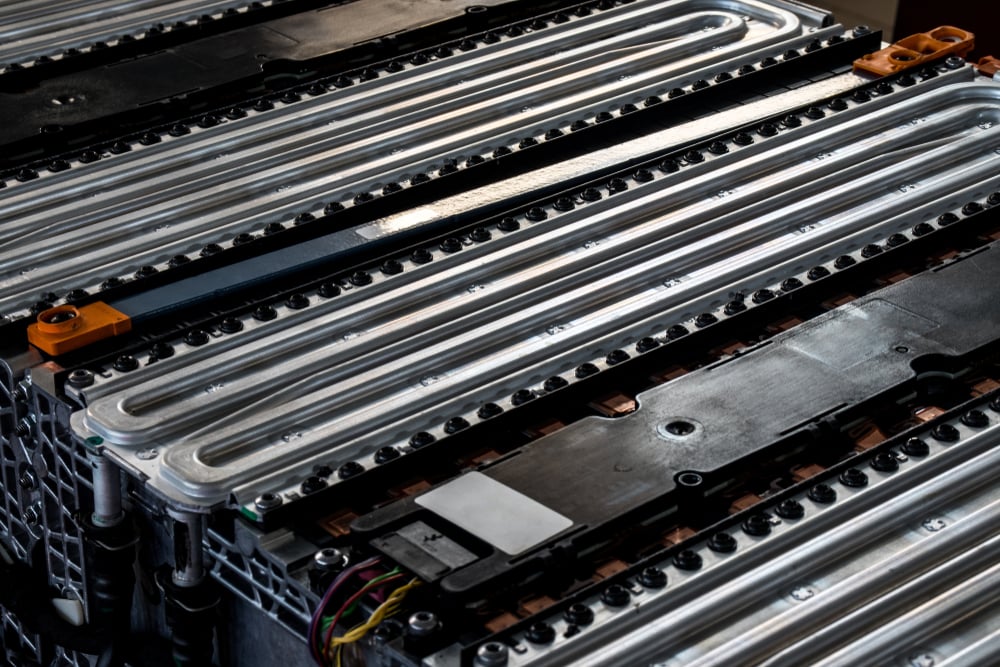

This process can also be accelerated by the use of a fan. Another method is to include a liquid cooling jacket around the battery pack. This is very similar to cars, where a coolant circulates through the engine and dumps the heat into the radiator.
Battery Pack Casing Material
Battery packs consist of many cells connected together to maximize output voltage and capacity. However, they cannot be stored openly with other moving components and must therefore be held in a strong box within the vehicle’s chassis. Since battery packs heat up during the course of both charging and discharging, it is advantageous to have a casing that can direct heat away from them.

At the same time, it must be sturdy enough to deal with road surface and climatic irregularities in the region it serves. Thus, popular choices include plastics and metal. While plastics make for rigid, lightweight structures, they are poor conductors of heat. Metal, while being good conductors of heat, can be quite bulky and expensive.
How Does This Affect Electric Scooter Design?
A scooter has several design and cost constraints due to their compact, lightweight and affordable architecture. While liquid cooling and metallic battery casings are desirable for their superior cooling properties, they are quite bulky. Thus, the reliance on plastic and aluminum battery casings, alongside cooling by surrounding air, is the only viable solution at present.

In tropical regions, where ambient temperatures are quite high, very little heat gets transferred from the battery pack, accelerating thermal runaway. Built-in battery management systems sometimes fail to initiate a cutoff, causing the temperature spikes to worsen and result in a fire.
What Can Be Done To Prevent EV Fires?
Fires arising from lithium-ion battery packs are notoriously difficult to put out. Thus, manufacturers must rigorously test their batteries and associated systems for proofing against thermal runaway. Some of these include overheating warnings and cutoffs that isolate the battery pack to prevent it from further loading.

As end users, there are some things we can do to stay safe. Amongst the most important things is to monitor the state of charge of vehicles and not overcharge them. Another is to refrain from using driving modes that excessively load the battery in return for performance, when driving in less than optimum temperature conditions.
References (click to expand)
- (2014) Understanding Lithium Ion Battery Fires - OSTI.GOV. The Office of Scientific and Technical Information
- Gao, A., Dong, W., Xu, . fang ., Xu, X., & Fan, L. (2022, February 1). Study on Thermal Runaway Behavior of Lithium Ion Battery under Overcharge Using Numerical Detecting Method. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing.
- T Cai. Detection of Lithium-ion Battery Failure and Thermal Runaway. deepblue.lib.umich.edu












