Table of Contents (click to expand)
Rust is a poor conductor of electricity because it is an ionic compound in which the ions are not free to move.
If you’ve ever used old batteries to power a device, you might have noticed that they don’t always sufficiently power the item. On closer inspection, you may even find orange-red flakes covering the terminals. After removing these flakes, the device should work just fine.
However, why did those flakes develop on the cell and why did the battery not supply sufficient power before removing the flakes?

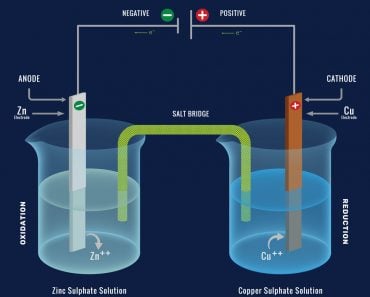
The branch of science that answers these questions is electrochemistry.
Recommended Video for you:
A Word About Conduction
The property of matter that allows a directional flow of electric charge carriers due to the application of a potential difference is called electrical conduction. This directional flow of charge carriers with time is called electric current. Conductivity is an intrinsic property (depending only on its internal structure) and is quantified as follows:
Conductivity of a material,  , is the current that flows through a 1 m long sample that is 1 m2 by cross section when a unit voltage (1 volt) is applied. Mathematically, the relation is expresses as follows:
, is the current that flows through a 1 m long sample that is 1 m2 by cross section when a unit voltage (1 volt) is applied. Mathematically, the relation is expresses as follows:
 where,
where,
I = Current (measured as output)
V = Applied voltage (input)
l = length of sample
a = area of cross section
Since conduction is a measure of the flow of charges, only those materials that contain free charge carriers (ions, electrons, protons) can conduct electricity.
Chemistry Of Rust
Rust is the chemical product of a redox reaction between metallic iron and oxygen in the presence of water ,which acts as a catalyst (speeds up the reaction speed). Iron gets oxidized to various iron oxides, which range from orange-brown to red in color. Rust is the general name referring to all these iron oxides and iron hydroxides.
Rust Chemical Reaction
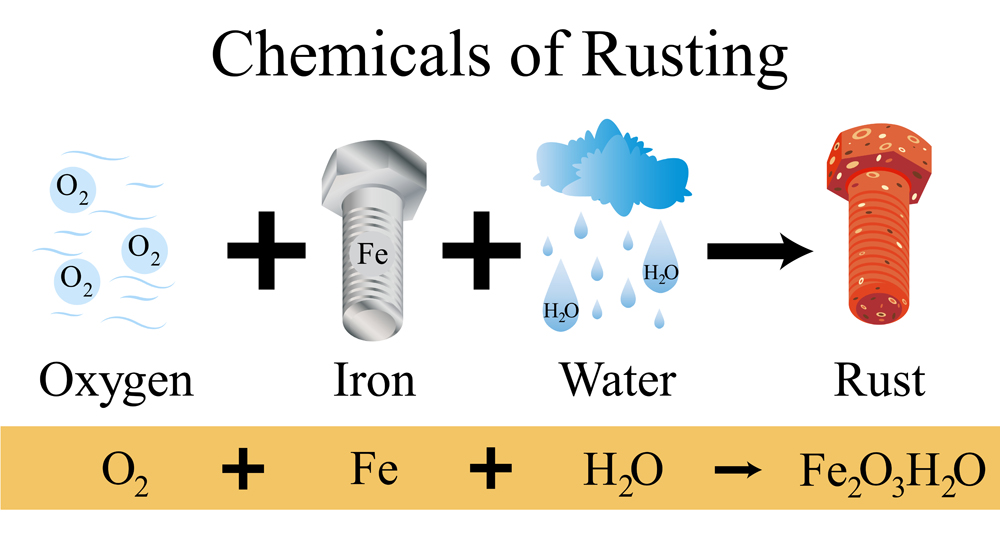
The reaction for rust formation consists of various sub-reactions that dictate the speed of reaction and the formation of rust. This is a redox reaction where Iron gets oxidized and Oxygen gets reduced. The reactants involved are metallic iron (Fe), Oxygen gas from the atmosphere (O2) and water vapor/moisture (H2O).
- Fe(s) ——> Fe2+(aq) + 2e– : In this step, solid iron loses two electrons (oxidizes) in the presence of moisture
- 4Fe2+(aq) + O2 ——> 4Fe3+ + 2O2- : Further oxidation of Fe2+ occurs due to presence of atmospheric oxygen
- O2 + 4 e− + 2H2O ——> 4 OH− : The electrons released from the oxidation of Fe reduce Oxygen to OH–
- Fe2+ + 2H2O ⇌ Fe(OH)2 + 2H+ : Fe2+ ions in water get hydrated to Fe(OH)2
- Fe3+ + 3H2O ⇌ Fe(OH)3 + 3 H+ : Fe3+ ions in water get hydrated to Fe(OH)3
- Fe(OH)2 ——> FeO + H2O : When water is removed (dehydration), FeO and Fe2O3 are formed
- 2FeO ——> Fe2O3 + H2O
Rust is the general term for Fe(OH)2, Fe(OH)3, FeO, Fe2O3 and higher oxides and hydroxides of Iron.
Nature Of Chemical Bonds
Recall that conductivity is a property that results from the ordered movement of charge carriers due to voltage. Charge carriers can be ions, electrons or protons. If free charge carriers don’t exist, then no current will flow upon the application of voltage.
About The Ionic Bond
Fe(OH)2, Fe(OH)3, FeO and Fe2O3 are all ionic compounds. Ionic compounds are formed when a metal atom (Fe) donates electrons to a non-metal atom. The metal atom gains a positive charge and the non-metal atom gains a negative charge, resulting in the formation of ions. This causes electrostatic attraction between the two oppositely charged ions. This attraction keeps the ions close, and this bond is called an ionic bond. The compounds formed due to the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are called ionic compounds.
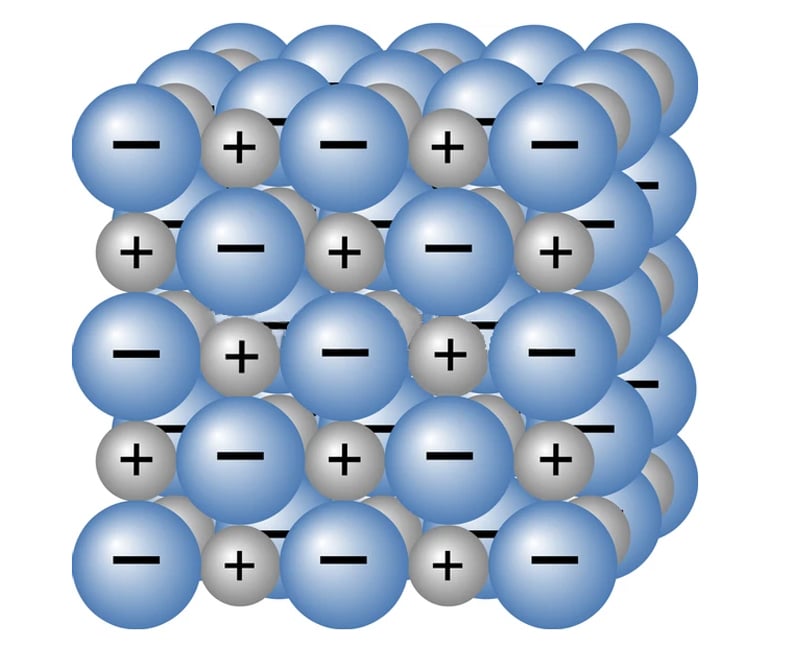
Why Is Rust An Insulator?
When in an aqueous solution, molten or gaseous form, ions are free to move, thereby conducting electricity. However, when in solid phase, ions are not free to move, and are instead bound together strongly to form crystals. The tendency of ions/charge carriers to move in the presence of voltage is called mobility.
Since conductivity arises due to the motion of charge carriers, there exists some characteristic velocity, called drift velocity, Vd, with which charge carriers move. The greater the drift velocity, the greater the current. Also, a voltage produces an electric field, E. Mobility is defined in terms of Vd and E as:

Since ions are not free to move in solid crystals, rust cannot conduct electricity!
References (click to expand)
- The Rusting Rates of Iron Nails - CSUN. California State University, Northridge
- Rust chemistry - Corrosion-Doctors.org. corrosion-doctors.org
- Textbooks PDF (I-XII) - NCERT. National Council of Educational Research and Training
- Ionic bonding | School of Materials Science and Engineering. University of New South Wales